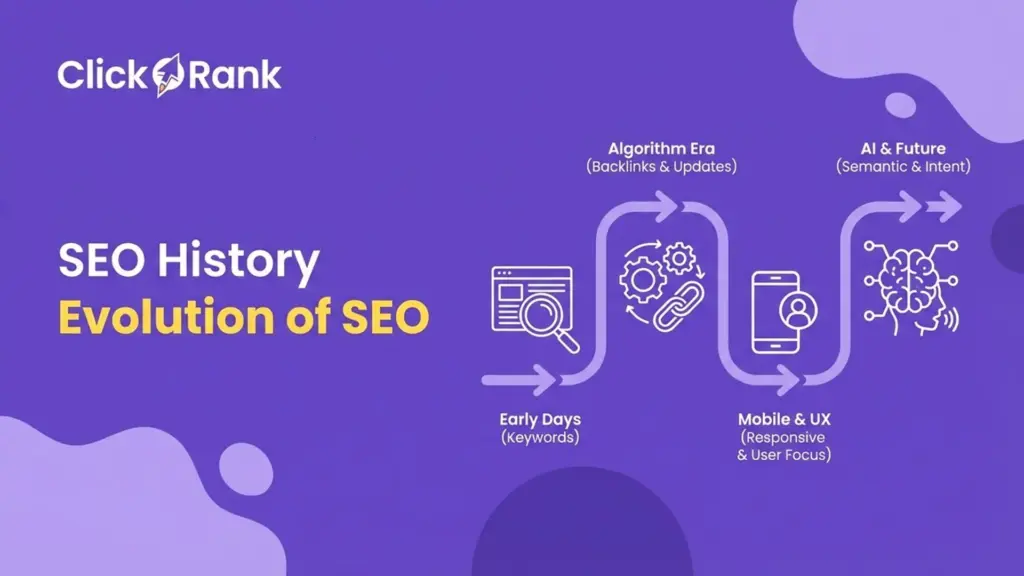
People don’t search the way they used to, and that’s exactly why many websites stop working. How people search online today is shaped by intent, emotion, devices, and AI not just keywords. Users ask questions, scan results fast, switch platforms, and expect instant answers. If your content still assumes users type short keywords and read long intros, you lose visibility.
This guide breaks down user search behaviour, explains why people search, and shows how search intent SEO works across Google, social platforms, and AI tools. You’ll learn how search queries form, how intent changes during the journey, and how modern engines interpret meaning instead of words.
SEO Basics, helping you understand the human side of search so you can create content that ranks, gets cited, and actually helps users.
What Does “How People Search” Actually Mean Today?
“How people search” today means users express intent, problems, or goals not just keywords. People now search using questions, voice commands, partial thoughts, and follow-up queries across Google, social apps, and AI tools.
This shift matters because search engines no longer rely on exact words. They analyze user search behaviour, context, device, and previous actions to understand meaning. For 2026 and beyond, engines reward content that answers why people search, not content that repeats keywords.
The practical impact is simple: if your content mirrors real human thinking, it gets surfaced more often. Pages that explain clearly, answer directly, and match real search intent SEO patterns win visibility across classic SERPs and AI-driven results.
Is search still just typing keywords into Google?
No, search is no longer limited to typing short keywords into Google. Users now search using full questions, voice commands, images, social platforms, and AI assistants.
This change matters because keyword-only optimization misses most modern search query types. People search by speaking naturally, scrolling visually, or asking AI tools follow-up questions. Google also rewrites queries internally to match intent, not wording.
In practice, this means content should match how users think, not how tools used to work. Use natural language, question-based headings, and clear answers. When your content sounds like the user’s own question, it aligns with real how people search online behavior and performs better.
How has search behavior changed in the last 5–10 years?
Search behavior has shifted from keyword hunting to intent discovery. Users now expect engines to understand vague, incomplete, or conversational queries.
This matters because people no longer plan searches carefully. They start broad, refine fast, and rely on engines to guide them. Mobile search behavior, voice search patterns, and AI tools have trained users to search casually and iterate.
The practical takeaway is to structure content for scanning and refinement. Answer early, support with depth, and allow users to jump sections. Content that supports evolving intent performs better across modern discovery systems.
Why understanding search behavior matters more than rankings?
Understanding search behavior matters more than rankings because visibility now depends on intent match, not position. Users interact with snippets, AI answers, videos, and summaries before clicking anything.
This matters for SEO because ranking first doesn’t guarantee attention. Engines reward content that satisfies intent quickly, keeps users engaged, and supports follow-up needs. Engagement signals now outweigh raw keyword placement.
Practically, businesses that map content to user intent win long-term. When you understand why people search, you create content that earns trust, citations, and recall making rankings a result, not the goal.
How Did People Search Before Modern Search Engines?
Before modern search engines, people searched by navigating manually, not by intent-based queries. Early users relied on directories, portals, bookmarks, and basic keyword searches to find information.
This matters because early search was effort-heavy and system-driven. Users adapted their behavior to how tools worked, not the other way around. There was no deep understanding of user search behaviour, only simple matching of words on pages.
The practical takeaway is important for today’s SEO. Search has flipped. Systems now adapt to humans. Understanding this shift helps explain why modern how people search online focuses on intent, clarity, and usefulness not technical tricks.
How did early internet users find information?
Early internet users found information by browsing directories, links, and basic search engines. They often clicked through categories instead of typing questions.
This mattered because search was discovery-based, not answer-based. Users explored pages manually and accepted slower results. Search query types were short, rigid, and often inaccurate.
Practically, this shows why structure still matters. Clear categorization, logical hierarchy, and scannable content helped users then and still helps today. Modern engines evolved, but human scanning behavior stayed the same.
What role did directories and portals play?
Directories and portals acted as human-curated maps of the internet. Sites like Yahoo Directory organized content into categories, making browsing the primary way to search. Users trusted editors, not algorithms, to decide what was relevant.
This shaped behavior by forcing users to think in categories, not questions. You didn’t ask “how to fix a printer” you browsed “Technology → Hardware → Printers.” This made discovery slower but more intentional.
The lesson for modern SEO is clear structure. Even today, engines reward well-organized content clusters. Clear topical grouping still helps AI and users understand relevance faster.
How did keyword stuffing shape early search behavior?
Keyword stuffing trained users and creators to game systems instead of helping people. Pages repeated terms unnaturally to rank, and users learned to type awkward phrases to get results.
This damaged trust and reduced content quality. Search engines responded by evolving toward intent-based understanding. That shift directly led to modern search intent SEO.
The practical insight is simple: tricks stop working. Systems always adapt. Content that focuses on real meaning survives longer than content built for loopholes.
What lessons from early search still apply today?
The biggest lesson is that clarity and structure always win. Even before AI, users preferred pages that were easy to scan and clearly organized.This matters because while technology changed, human behavior didn’t. People still skim, compare, and refine searches. Modern engines just automate that process.
Practically, content should be clean, focused, and structured for understanding. When you respect how people process information, your content stays relevant across every search evolution.
How Do People Search Today Across Different Platforms?
People search today by expressing intent across platforms, not just typing exact keywords into one engine. Search now happens on Google, social apps, marketplaces, and AI tools, often in short bursts and follow-up actions.
This matters because how people search online is no longer linear. Users jump between devices, rephrase queries, and expect systems to “get it” instantly. Google and other platforms analyze user search behaviour, context, and past interactions to predict intent.
The practical impact is clear: content must be flexible and intent-led. Pages that answer clearly, adapt to multiple search query types, and support quick understanding perform better across modern discovery systems.
How do people search on Google now?
People search on Google now using natural language, partial thoughts, and evolving questions. Instead of perfect keywords, users type what comes to mind and refine based on results.
This shift matters because Google focuses on meaning, not wording. It uses intent signals, SERP interaction, and behavior patterns to understand why people search, even when queries are unclear. Mobile search behavior has accelerated this trend, making searches faster and more casual.
Practically, content should answer early and clearly. Use question-based headings, simple language, and direct responses. When your page matches how users naturally ask things, it aligns better with modern search intent SEO and earns stronger visibility.
Why are searches longer and more conversational?
Searches are longer because users trust engines to understand natural language. Voice search patterns, mobile typing, and AI assistants encourage people to search the way they speak.
This matters because conversational search reveals clearer intent. A query like “best budget phone for students” shows needs, limits, and context all in one line. Engines extract these signals to deliver precise answers.
For content creators, this means writing like a human. Use plain language, complete thoughts, and realistic phrasing. Content that sounds natural fits modern keyword phrasing behavior and performs better in AI-driven results.
How does Google interpret vague or incomplete queries?
Google interprets vague queries by using context, patterns, and prediction models. It looks at location, device, recent searches, and how similar users behave to infer intent.
This matters because users don’t need perfect queries anymore. Searches like “best one” or “near me” are expanded internally to match likely needs. Google tests results and adjusts based on clicks and engagement.
Practically, your content should support ambiguity. Cover related questions, explain basics clearly, and anticipate follow-ups. This helps your page match inferred intent and stay visible even when queries are unclear.
How do people search on social platforms (TikTok, Instagram, YouTube)?
People search on social platforms by exploring visuals, creators, and trends instead of typing formal queries. Users rely on videos, comments, and recommendations to discover answers.
This matters because social search is intent-driven but visually led. Users often search with short phrases like “gym routine” or “phone review” and then judge relevance by thumbnails, captions, and creator credibility. This reflects modern user search behaviour, where trust and relatability matter more than blue links.
Practically, content must be visual, fast, and clear. Titles, captions, and spoken words should match natural search query types. Brands that optimize for discovery inside feeds align better with how people actually search today.
Why are Gen Z users skipping Google?
Gen Z skips Google because social platforms feel faster, more human, and more trustworthy. They prefer seeing real people explain things instead of reading long articles.This shift matters because younger users associate search with discovery, not research. A TikTok video showing “how to style sneakers” feels more helpful than ten links. Social proof, comments, and creator identity replace traditional authority.
For businesses, this means adapting content formats. Clear explanations, authentic visuals, and short answers match why people search emotionally not just logically.
How visual and short-form search works?
Visual search works by matching intent through images, motion, and audio instead of text. Short videos act as both the query and the answer.This matters because users scan with their eyes first. Algorithms read captions, hashtags, spoken words, and engagement to match intent. This creates a new form of conversational search without typing.
Practically, clarity wins. Say the answer early, show the result fast, and support it visually. This mirrors modern how people search online across visual-first platforms.
How do people search inside AI tools like ChatGPT, Gemini & Perplexity?
People search inside AI tools by having conversations, not by entering isolated queries. Users ask follow-ups, refine intent, and expect synthesized answers.
This matters because AI search removes friction. Instead of ten searches, users ask one evolving question. AI tools analyze context across the conversation, not just the last input, changing search intent SEO completely.
Practically, content must support extraction. Clear answers, structured explanations, and entity clarity help AI tools retrieve and reuse your information accurately.
Why AI search is intent-first, not keyword-first?
AI search starts with understanding goals, not matching words. It identifies the problem, outcome, and constraints before generating answers.This matters because keywords become signals, not requirements. AI tools infer meaning even when users are vague or inconsistent. This reflects real user intent better than traditional search.
For content creators, the lesson is simple: answer the real question. Focus on usefulness, not phrasing tricks. Intent alignment now drives visibility.
How AI rewrites and expands user queries automatically?
AI rewrites queries by adding context users didn’t state. It expands vague inputs into structured internal questions before answering.This matters because users don’t need to be precise anymore. AI predicts missing details like location, experience level, or urgency. This changes how search patterns work.
Practically, content should cover related sub-questions naturally. When your page supports expanded intent, AI tools are more likely to surface it accurately.
What Are the Core Types of Search Intent?
The core types of search intent describe the real reason behind every search query. Instead of focusing on words, modern SEO focuses on why the user is searching and what outcome they expect.
This matters because search engines rank pages that best match intent, not pages that repeat keywords. Search intent SEO helps engines understand whether a user wants to learn, find a brand, or take action. If intent is mismatched, rankings and engagement fail even with strong optimization.
Practically, identifying intent helps you choose the right content format, depth, and CTA. When your content aligns with how people search online, it performs better in SERPs, AI answers, and voice results.
What is informational search intent?
Informational search intent means the user wants to learn or understand something. These searches are driven by curiosity, confusion, or the need for clear explanations not buying decisions.
This matters because most searches fall into this category. Queries like “how,” “why,” and “what” dominate search query types and shape early-stage discovery. Google and AI tools prioritize clear, structured answers for these queries.
In practice, content should teach first. Use direct answers, simple language, and examples. When you help users learn without pushing sales, you earn trust, engagement, and long-term visibility.
Why do “how”, “why”, and “what” searches dominate?
These searches dominate because they reflect natural human curiosity. People search to reduce uncertainty, solve problems, or understand unfamiliar topics before taking action.
This matters for SEO because engines are built to reward clarity. “How,” “why,” and “what” queries clearly signal learning intent, making them easier to satisfy with structured content.
Practically, this is why guides, FAQs, and explainers perform so well. When your content answers these questions directly, it aligns perfectly with user search behaviour and AI-driven retrieval systems.
How people search when they want to learn, not buy?
When users want to learn, they search broadly and safely. Queries are open-ended, neutral, and exploratory, such as “how does SEO work” or “what is search intent.”This matters because users are not ready for conversion. Pushing products here creates friction and lowers trust. Engines detect this mismatch through engagement signals.
Practically, learning-focused content should avoid sales pressure. Provide education, clarity, and next-step guidance. This builds authority and keeps your brand present as intent evolves.
What is navigational search intent?
Navigational search intent means the user wants to reach a specific website, brand, or platform. The goal is access, not discovery.
This matters because users already know where they want to go. Queries often include brand names, tools, or services instead of URLs. Engines prioritize accuracy and trust here.
Practically, strong brand signals matter most. Clear site structure, branded content, and trust indicators help users and engines reach the right destination faster.
Why brand names replace URLs?
Brand names replace URLs because they are easier to remember and type. Users trust search engines to handle navigation instead of recalling exact web addresses.This matters for visibility because branded searches signal authority. Engines see repeated brand-based queries as trust indicators within user intent patterns.
Practically, building brand recognition increases navigational traffic. When users search your name directly, you reduce reliance on competitive keyword rankings.
How trust influences navigational searches?
Trust drives users to search for brands they already believe in. Positive experiences, reviews, and familiarity shape these searches.This matters because trust-based searches convert better and bounce less. Engines recognize this through engagement and return visits.
Practically, credibility-building content, transparency, and consistency increase navigational searches making your brand the destination, not just another result.
What is commercial investigation intent?
Commercial investigation intent means the user is comparing options before making a decision. The goal is not to buy yet, but to evaluate choices, features, pricing, and credibility.
This matters because this intent sits between learning and buying. Users already understand the problem and now want the best option. Searches like “best SEO tool,” “ClickRank vs alternatives,” or “top laptops for students” show strong buying signals without urgency. Search engines treat these queries carefully and reward balanced, helpful comparisons.
Practically, content should guide not sell. Use comparisons, pros and cons, use cases, and clear explanations. When your content supports decision-making honestly, it aligns with real user search behaviour and performs strongly in search intent SEO.
Why comparison searches happen before buying?
Comparison searches happen because users want to reduce risk before spending money. They look for reassurance, proof, and differences that justify a choice.
This matters because buying online feels uncertain. Users search things like “X vs Y,” “best for beginners,” or “is it worth it” to validate decisions. These search query types show intent moving closer to conversion.
Practically, comparison content should be clear and unbiased. When you help users feel confident, engines reward your page with higher visibility and longer engagement.
How people evaluate options before conversion?
People evaluate options by checking features, reviews, pricing, and real-world fit. They compare what solves their problem best, not what ranks first.This matters because users scan fast. They look for summaries, tables, and direct answers. Overloaded or sales-heavy pages lose trust quickly.
Practically, show clarity. Highlight differences, explain who each option is for, and answer common doubts. This supports modern how people search online during decision-making.
What is transactional search intent?
Transactional search intent means the user is ready to take action now. This includes buying, booking, signing up, or contacting a business.This matters because intent is strongest here. Queries include words like “buy,” “price,” “discount,” or “near me.” Engines prioritize speed, accuracy, and relevance for these searches.
Practically, pages should remove friction. Clear CTAs, pricing visibility, and trust signals help users complete actions quickly and confidently.
Why urgency changes search wording?
Urgency makes searches shorter and more direct. Users drop explanations and focus on action-based terms.This matters because time pressure changes keyword phrasing behavior. Searches like “emergency plumber near me” or “same-day delivery” show immediate need.
Practically, content should recognize urgency. Clear availability, location, and next steps improve conversions and visibility.
How modifiers like “near me” and “best price” appear?
Modifiers appear when users want relevance and value fast. They narrow results by location, cost, or quality.This matters because these modifiers signal transactional intent clearly. Engines treat them as high-conversion queries.
Practically, optimize for these terms naturally. Location pages, pricing clarity, and trust cues help your content match urgent intent accurately.
How Do Emotions Influence How People Search?
Emotions strongly influence how people search by shaping wording, urgency, and repetition. When users feel stressed, curious, or uncertain, their searches become more emotional than logical.
This matters because modern search engines and AI systems read behavioral signals, not just text. Emotional states affect user search behaviour, click patterns, and follow-up queries. Search intent SEO now depends on understanding emotional context, especially for sensitive or high-stakes topics.
The practical impact is clear: content that acknowledges emotions performs better. Clear reassurance, calm language, and helpful structure improve engagement and trust making your content more visible across SERPs and AI answers.
Do people search differently when stressed, curious, or confused?
Yes, people search very differently based on emotional state. Stress creates urgent, fragmented searches. Curiosity leads to open-ended exploration. Confusion triggers repeated reformulation.
This matters because emotional state changes search query types. A stressed user types short, urgent phrases. A curious user asks broader “why” and “how” questions. Engines detect this through behavior and adjust results.
Practically, content should match the emotion. Use direct answers for stress, depth for curiosity, and step-by-step clarity for confusion. This aligns with how people search online in real moments.
Why emotional triggers create repetitive searches?
Emotional uncertainty causes users to search again and again for reassurance. When answers don’t fully resolve fear or doubt, users refine and repeat queries.
This matters because repetition signals unresolved intent. Engines see multiple similar searches as a cue to surface clearer, more authoritative answers. This is common in health, finance, and troubleshooting topics.
Practically, anticipate follow-ups. Address common fears, explain outcomes, and offer reassurance. When your content resolves emotion not just facts it reduces bounce and improves visibility.
How fear-based searches differ from curiosity-based searches?
Fear-based searches aim to reduce risk, while curiosity-based searches aim to expand knowledge. The intent, tone, and urgency are completely different.
This matters because fear searches include words like “safe,” “risk,” or “is it legit.” Curiosity searches use exploratory language. Engines treat fear queries more cautiously and prioritize trust.
Practically, fear-driven content needs credibility and calm explanations. Curiosity-driven content benefits from depth and examples. Matching emotion improves trust, engagement, and AI retrieval.
How Does Context Shape Search Behavior?
Context shapes search behavior by changing how, when, and why people search. Factors like device type, location, and time directly influence wording, urgency, and intent.
This matters because how people search online is never neutral. A user on a phone, in a hurry, or on the move behaves very differently from someone researching at a desk. Search engines and AI systems read these contextual signals to adjust results automatically.
The practical impact is clear: content must work across contexts. Pages that answer quickly for urgent searches and still support deeper exploration perform better in modern search intent SEO.
How does device type change how people search?
Device type changes search behavior by shaping speed, depth, and phrasing. Mobile users search fast and act quickly, while desktop users search more thoroughly.
This matters because user search behaviour varies by screen size and environment. Mobile searches often happen mid-task and are goal-focused. Desktop searches support comparison, learning, and longer sessions.
Practically, content should adapt to both. Clear headings, direct answers, and scannable sections support mobile users, while depth and structure support desktop research. This balance aligns with modern search query types.
Why mobile searches are shorter but more urgent?
Mobile searches are shorter because users are multitasking or on the move. They want quick answers with minimal effort.This matters because urgency drives intent. Queries like “near me,” “open now,” or “quick fix” dominate mobile search behavior. Engines prioritize speed and relevance for these searches.
Practically, answer immediately. Use concise language, visible CTAs, and location cues. This improves engagement and conversion for high-intent mobile users.
How desktop searches support deeper research?
Desktop searches support deeper research because users have time, space, and focus. They compare options, read long explanations, and evaluate credibility.This matters because desktop queries often signal informational or commercial investigation intent. Users scroll more, open multiple tabs, and analyze details.
Practically, provide structure and depth. Use sections, comparisons, and clear explanations. When your content supports deep research, it performs better across long-form and AI-driven discovery.
How does location affect search phrasing?
Location affects search phrasing by adding local context, urgency, and relevance to queries. Users naturally include city names, neighborhoods, or proximity cues when results depend on where they are.
This matters because search engines heavily weight local signals. Queries like “coffee shop,” “dentist,” or “SEO service” change meaning based on location. Google and AI tools infer intent even when users don’t state a place directly, using IP, GPS, and past behavior.
Practically, content should reflect local language and needs. Pages that mention service areas, landmarks, and local relevance align better with real user search behaviour and perform stronger in local discovery.
Why “near me” searches keep growing?
“Near me” searches grow because users want fast, convenient solutions without typing full locations. Mobile usage and GPS accuracy make proximity-based search effortless.
This matters because “near me” signals high intent. Engines treat these searches as action-ready and prioritize local relevance over generic authority.Practically, businesses should optimize location signals. Clear addresses, local pages, and proximity cues help content match urgent how people search online patterns.
How local intent overrides generic intent?
Local intent overrides generic intent when location becomes the deciding factor. A user searching “best pizza” wants different results in New York than in London.This matters because engines rewrite queries internally. Even broad searches get localized automatically when context suggests local need.
Practically, content should balance authority with locality. When your page matches both topic and place, it wins local visibility over generic competitors.
How does time influence search behavior?
Time influences search behavior by changing urgency, mindset, and intent. People search differently based on time of day, week, or year.
This matters because searches reflect current needs. Daytime searches are task-driven, while nighttime searches are more reflective or exploratory. Engines detect these patterns through behavior data.
Practically, understanding timing helps you match intent better. Content aligned with time-based needs performs stronger in modern search intent SEO.
Why people search differently at night vs daytime?
At night, users search more emotionally and casually. During the day, searches are practical and goal-focused.This matters because intent shifts. Night searches often involve learning, reassurance, or planning. Day searches focus on action and productivity.
Practically, content should support both. Clear explanations help night users, while direct answers and CTAs help daytime intent.
How seasonality impacts intent?
Seasonality impacts intent by changing what people care about at different times of year. Needs rise and fall based on events, weather, and trends.This matters because search demand shifts predictably. Engines expect content to stay relevant to seasonal intent.
Practically, updating content for seasonal context improves visibility and engagement. Timely relevance keeps your content aligned with evolving search patterns.
How Do Voice Searches Change the Way People Search?
Voice searches change how people search by making queries more natural, conversational, and intent-rich. When users speak, they ask full questions instead of typing short phrases.
This matters because voice search reveals real user search behaviour. People talk the way they think, not the way search engines used to work. AI and search engines now prioritize meaning, context, and clarity over exact wording.
The practical impact is clear: content must sound human. Pages that answer questions directly, use simple language, and match spoken phrasing perform better in voice results and AI-driven discovery.
Why do voice searches sound like full questions?
Voice searches sound like full questions because speaking feels natural and effortless. Users don’t shorten thoughts when talking; they explain the problem fully.
This matters because full questions carry strong intent signals. A spoken query like “how do I fix a slow website on mobile” gives engines clear context. This improves accuracy and result quality.
Practically, content should mirror spoken language. Question-based headings and direct answers align with how people search online through voice and AI assistants.
How do people phrase searches when talking vs typing?
When talking, people use natural sentences; when typing, they shorten and simplify. Spoken searches include fillers, context, and intent cues.This matters because engines now normalize both forms. Voice input helps systems learn real phrasing patterns and improve search intent SEO.
Practically, write naturally. Use complete thoughts, simple explanations, and everyday language. Content that works when read aloud also performs better in AI summaries.
What types of content win voice search results?
Content that wins voice search delivers clear, direct answers fast. Voice assistants prefer concise, structured responses they can read aloud.
This matters because voice results usually show only one answer. Pages with definitions, FAQs, and step-by-step explanations are favored.
Practically, lead with the answer, then explain. Use clear formatting and simple sentences. This makes your content easier to extract, speak, and trust.
How Do People Search When They Don’t Know What to Ask?
People search without clear questions by starting vague and refining as they go. When users don’t fully understand a problem, they rely on search engines to guide discovery.
This matters because uncertainty is common in how people search online. Users often feel confused, new to a topic, or unsure of terminology. Google and AI tools are designed to interpret these signals and help users clarify intent step by step.
The practical impact is big for SEO. Content that supports exploration, explains basics clearly, and anticipates follow-ups aligns better with real user search behaviour and performs stronger in modern search.
Why do users start with vague or broken queries?
Users start with vague or broken queries because they don’t yet know the right words. They search with fragments, partial ideas, or generic terms to test understanding.
This matters because early searches are exploratory, not precise. Queries like “SEO thing,” “website problem,” or “ranking down” reflect uncertainty, not lack of intent. Engines use these signals to surface broad, educational results.
Practically, content should be forgiving. Use plain language, define terms clearly, and avoid jargon. This helps your page match unclear search query types and guide users forward.
How Google and AI interpret unclear searches?
Google and AI interpret unclear searches by predicting intent using context and patterns. They analyze past behavior, similar users, and engagement signals to guess meaning.
This matters because users don’t need perfect input anymore. Engines rewrite queries internally and test results based on reactions. AI tools expand vague prompts into structured questions.
Practically, content should cover related concepts naturally. When your page supports multiple interpretations, it becomes more useful and more retrievable.
How follow-up searches reveal real intent?
Follow-up searches expose what the user actually wants. Each refinement removes uncertainty and sharpens intent.This matters because engines track these sequences. A user moving from “SEO basics” to “how to optimize titles” shows clear learning progression.
Practically, structure content to support this journey. Answer the main question, then guide to next steps. This keeps users engaged and aligns with evolving intent.
How Search Evolves During the Buyer’s Journey?
Search evolves during the buyer’s journey by becoming more focused, specific, and action-driven over time. Users don’t jump straight to buying; they search in stages as understanding grows.
This matters because how people search online mirrors decision-making. Early searches explore problems, mid-stage searches compare options, and late-stage searches confirm choices. Search engines and AI tools track these shifts through behavior patterns.
The practical impact is clear for SEO. Content must match each stage. When pages align with real user search behaviour at the right moment, they earn trust, engagement, and conversions naturally.
How do searches look at the awareness stage?
At the awareness stage, searches are broad, educational, and problem-focused. Users try to understand what’s wrong or what they need.This matters because intent is low-pressure. Queries include “what is,” “why does,” or “how does.” Users aren’t ready to buy; they want clarity. Engines prioritize helpful explanations and beginner-friendly content.
Practically, content should teach, not sell. Define problems, explain concepts, and use simple examples. This builds credibility and keeps your brand visible early in the journey.
How do searches evolve during consideration?
During consideration, searches become more specific and comparative. Users now know the problem and are evaluating solutions.This matters because intent strengthens. Queries include “best,” “vs,” “reviews,” or “pricing.” Search engines reward balanced, informative content that helps decision-making.
Practically, provide comparisons, use cases, and honest pros and cons. When you help users evaluate options, you align with real search intent SEO and stay relevant mid-journey.
How do decision-stage searches become highly specific?
At the decision stage, searches are precise and action-oriented. Users know what they want and look for final confirmation.This matters because queries include brand names, locations, and transactional terms. Engines prioritize trust, clarity, and ease of action.
Practically, content should remove friction. Clear CTAs, pricing, and reassurance help users act confidently. Matching this intent drives conversions and long-term trust.
How Do People Search for Trust and Credibility?
People search for trust and credibility by actively validating sources before believing or choosing them. Instead of accepting results at face value, users now look for proof signals that confirm safety, quality, and reliability.
This matters because modern user search behaviour is cautious. Scams, misinformation, and low-quality content have trained users to double-check claims. Search engines and AI tools respond by prioritizing trusted brands, expert sources, and verified information especially in sensitive topics.
The practical impact is clear: credibility is no longer optional. Content that shows expertise, transparency, and real-world validation aligns with how people search online and earns stronger visibility, clicks, and AI citations.
Why do users add “reviews”, “ratings”, and “is it legit”?
Users add trust modifiers because they want reassurance before committing time, money, or belief. These words signal doubt and a need for validation.
This matters because trust checks often happen right before decisions. Queries like “tool reviews,” “company ratings,” or “is it legit” show high intent mixed with caution. Search engines treat these as credibility-focused search query types.
Practically, content should answer trust questions directly. Show reviews, explain pros and cons honestly, and address common concerns. When you reduce doubt, you increase engagement and confidence.
How does brand authority influence click behavior?
Brand authority strongly influences which results users click. When users recognize or trust a name, they are more likely to choose it even if it’s not ranked first.
This matters because users scan fast. Familiar brands feel safer, especially in crowded SERPs. Engines also detect this behavior and reinforce authority through higher visibility.
Practically, consistent branding, clear expertise, and reliable content build recognition. Over time, users search for you directly, reducing dependence on rankings alone.
Why expertise matters more in YMYL searches?
Expertise matters most in YMYL searches because the consequences are real. Topics involving health, money, or safety require higher trust standards.
This matters because users are more cautious. Engines prioritize expert-backed content, clear sourcing, and accuracy to protect users from harm.
Practically, show credentials, cite reliable sources, and explain carefully. When your content demonstrates real expertise, it earns trust from both users and search systems.
How Do Search Engines Understand How People Search?
Search engines understand how people search by analyzing intent, behavior, and patterns not just words. Modern systems focus on what users are trying to achieve rather than the exact phrasing they use.
This matters because how people search online is messy and inconsistent. Users change wording, refine queries, and behave differently based on context. Search engines observe these signals to interpret user search behaviour accurately and deliver better results.
The practical impact for SEO is major. Content that aligns with intent, satisfies users quickly, and supports follow-up needs is more likely to rank, get cited, and stay visible across AI-driven search experiences.
How does Google use intent signals instead of exact keywords?
Google uses intent signals to understand meaning beyond exact keywords. It analyzes query patterns, context, and historical behavior to infer what the user wants.
This matters because keyword matching alone fails with conversational and vague searches. Google looks at query refinements, SERP interaction, device type, and location to determine intent. This allows it to serve relevant results even when wording is unclear.
Practically, content should focus on answering real questions. Clear explanations, topic coverage, and natural language help Google match your page to multiple search query types without keyword stuffing.
What role do engagement metrics play?
Engagement metrics tell search engines whether results actually help users. Clicks, dwell time, scrolling, and return behavior act as feedback signals.This matters because engines test and learn. If users quickly leave a page, it signals mismatch. If they stay, scroll, or refine less, it signals satisfaction.
Practically, improve readability and usefulness. Answer early, structure clearly, and support deeper exploration. Strong engagement reinforces intent alignment and improves long-term visibility.
How does machine learning predict what users want next?
Machine learning predicts next intent by analyzing large-scale behavior patterns. It studies how millions of users move from one query to another.This matters because search is no longer isolated. Engines anticipate follow-ups and surface results proactively. AI tools even combine multiple searches into one response.
Practically, structure content for journeys, not single queries. When your content supports natural next steps, it becomes more discoverable and reusable by AI systems.
How Does AI Change Search Discovery Completely?
AI changes search discovery by turning searching into direct answering. Instead of showing links, AI systems now summarize, combine, and explain information in one response.
This matters because how people search online is becoming frictionless. Users expect instant clarity, not ten tabs. AI tools analyze user search behaviour, context, and follow-ups to deliver complete answers in one interaction.
The practical impact is huge for SEO. Visibility now depends on whether your content is used by AI, not just clicked. Content that is clear, structured, and intent-aligned is more likely to be surfaced and cited.
Why AI search removes the need for multiple clicks?
AI search removes multiple clicks by synthesizing information instantly. Users get answers without visiting several pages.This matters because traditional browsing is slow. AI reads many sources, extracts key points, and delivers a single response. This matches modern expectations for speed and clarity.
Practically, content must be extractable. Clear answers, definitions, and logical structure increase the chance your content is included in AI summaries.
How AI merges multiple searches into one answer?
AI merges searches by understanding intent across queries. It connects related questions and fills gaps automatically.This matters because users often search in steps. AI tools collapse these steps into one response, saving time and effort.
Practically, cover topics holistically. When your content answers core questions and related sub-questions, AI can reuse it more effectively.
Why content must now answer before the user asks?
Content must answer early because AI anticipates intent. Systems predict what users need next and surface answers proactively.This matters because waiting to explain later reduces visibility. AI favors content that resolves uncertainty immediately.
Practically, lead with answers, then expand. This approach aligns with modern search intent SEO and keeps your content relevant in AI-first discovery.
How Should Content Be Structured Based on How People Search?
Content should be structured to deliver answers immediately, not slowly build up to them. Modern users and AI systems both scan for clarity before committing attention.
This matters because how people search online is fast and impatient. Users skim, AI extracts, and engines reward content that resolves intent quickly. Long introductions delay value and reduce engagement across SERPs and AI summaries.
The practical impact is simple: structure for access. Clear sections, direct answers, and logical flow help content perform better in search intent SEO, voice search, and AI-driven discovery.
Why direct answers matter more than long intros?
Direct answers matter because users want solutions, not buildup. Searchers decide within seconds whether content is useful.
This matters because engines track engagement. Pages that answer immediately reduce pogo-sticking and increase satisfaction signals. AI tools also prefer content with clear, early answers.
Practically, lead with the answer, then explain. This keeps users engaged and improves extractability across modern search systems.
How question-based headings match real search behavior?
Question-based headings mirror how users actually think and search. Most searches are phrased as questions, even when typed briefly.This matters because headings act as intent signals. Search engines and AI tools scan headings to match queries quickly. Clear questions improve relevance and snippet eligibility.
Practically, use real user questions as headings. This aligns structure with search query types and improves both readability and discoverability.
How chunked content improves AI and human readability?
Chunked content improves readability by breaking information into clear, focused sections. Both humans and AI prefer manageable pieces.This matters because large blocks hide meaning. Chunking helps AI extract accurate answers and helps users scan faster.
Practically, use short paragraphs, clear subheadings, and focused sections. This structure supports user search behaviour and increases long-term visibility.
How Can Businesses Align With How People Search?
Businesses align with how people search by prioritizing intent, clarity, and usefulness over keyword tricks. Modern search rewards content that genuinely helps users achieve goals.
This matters because how people search online has shifted toward intent-driven discovery. Users ask questions, compare options, and expect fast answers. Search engines and AI systems now evaluate how well content satisfies real user search behaviour, not just rankings.
The practical impact is strong. Businesses that design content around intent earn trust, visibility, and conversions across SERPs and AI answers without chasing unstable algorithms.
How to map content to real search intent?
Mapping content to real search intent starts with understanding the user’s goal. Each page should serve one clear purpose.This matters because mixed intent confuses both users and engines. Identify whether the user wants to learn, compare, or act, then match content format to that need.
Practically, group topics by intent, not keywords. Use clear answers for informational intent, comparisons for investigation, and CTAs for transactional searches. This alignment improves engagement and relevance.
Why keyword volume alone is misleading?
Keyword volume is misleading because it ignores intent and quality. High-volume terms often mix multiple intents.This matters because chasing volume attracts the wrong audience. Users bounce when content doesn’t match expectations, sending negative signals to engines.
Practically, prioritize intent clarity over traffic size. Lower-volume, high-intent queries often drive better results and stronger trust.
How to optimize for humans first, algorithms second?
Optimizing for humans first means writing clearly, honestly, and helpfully. Algorithms now follow user satisfaction.This matters because engines learn from behavior. Content that helps people naturally performs better long-term.Practically, focus on solving problems, answering questions early, and building trust. When humans win, algorithms follow.
How Will People Search in the Next 3–5 Years?
People will search less manually and rely more on AI-assisted discovery. Search will shift from typing queries to receiving proactive, conversational answers.
This matters because how people search online is evolving toward convenience and prediction. Users want fewer steps, faster clarity, and less effort. AI systems will increasingly anticipate needs based on behavior, context, and preferences.
The practical impact is clear: visibility will depend on how well content supports AI understanding. Businesses that structure content for intent, clarity, and reuse will stay discoverable as search continues to evolve.
Will traditional search results decline?
Yes, traditional search results will decline in influence, not disappear. Users will still see SERPs, but they will rely on them less.This matters because AI summaries, voice answers, and featured responses reduce the need to click links. Users get answers directly without browsing multiple pages.
Practically, content must be summary-ready. Clear answers, structured sections, and credibility increase the chances of being included in AI-driven results.
How AI agents will search on behalf of users?
AI agents will search by acting as decision-makers, not just tools. They will gather, compare, and summarize information automatically.This matters because users will delegate searching tasks. AI agents will evaluate options based on preferences, trust, and past behavior.
Practically, content should be machine-readable and decision-friendly. Clear explanations, comparisons, and trust signals help AI choose your content.
Why “search” will feel more like conversation than browsing?
Search will feel conversational because users will interact through dialogue, not clicks. AI will ask follow-up questions and refine answers in real time.This matters because conversation mirrors human thinking. Users won’t plan queries; they’ll talk naturally.
Practically, write content that sounds human. Natural language, clear answers, and logical flow make your content usable in conversational search.
Why Understanding How People Search Is the Foundation of SEO & AI Visibility
Understanding how people search is the foundation of SEO and AI visibility because intent drives discovery. Rankings alone no longer guarantee traffic, trust, or citations.
This matters because how people search online now spans Google, social platforms, and AI tools. Engines evaluate whether content truly satisfies user search behaviour, not just where it ranks. AI systems reuse content that explains clearly and matches real intent.
The practical impact is long-term visibility. When content is built around intent and clarity, it stays relevant across algorithm changes, AI summaries, and future discovery systems.
Why ranking without intent understanding fails?
Ranking without intent understanding fails because users don’t find what they expect. Even top positions lose clicks if intent is mismatched.This matters because engines track dissatisfaction. Quick exits, rewrites, and follow-up searches signal failure. Over time, rankings drop.Practically, intent alignment must come first. When your content answers the real question, rankings follow naturally.
How search behavior knowledge future-proofs content?
Search behavior knowledge future-proofs content by making it adaptable. Intent-based content survives platform changes.This matters because algorithms evolve, but human behavior stays consistent. AI tools still rely on intent clarity.Practically, build content around problems, questions, and outcomes not trends. This keeps your content reusable and visible long-term.
Why search will always start with human curiosity?
Search always starts with curiosity because humans seek understanding. Technology only changes how that curiosity is expressed.This matters because curiosity drives questions, exploration, and learning. Engines exist to serve that need.Practically, content that respects curiosity by teaching clearly and honestly will always win in search and AI visibility.
How are people’s search queries changing in 2025?
People are no longer relying on short keyword phrases. Instead, they are using longer, more conversational queries such as full questions. These complex searches trigger different outcomes, including AI Overviews. Data shows that queries with seven or more words trigger AI summaries nearly 46% of the time, compared to about 9.5% for shorter queries.
How common are AI-driven summaries in search results now?
AI-generated summaries, known as AI Overviews, now appear for a large share of searches. According to Ahrefs data, AI Overviews show up in roughly 20–55% of searches by volume, highlighting a major shift toward answer-first search experiences.
Why are zero-click searches increasing?
Zero-click searches happen when users get their answer directly on the search results page without clicking any website. This trend is growing because SERP features like featured snippets and AI Overviews provide instant answers. Studies show zero-click rates increasing as summarized information appears more often at the top of the page.
How is AI changing where people search besides Google?
AI tools such as ChatGPT are changing search behaviour beyond traditional engines. Clickstream research by Semrush found that prompts used without search-style modes were much longer, averaging around 23 words, while search-like prompts were much shorter, around four words. This shows people use AI for both deep exploration and quick fact finding.
Are people switching from traditional search engines?
Yes. Adoption of generative AI search is increasing. Surveys and behavioural data suggest that traditional search engines are slowly losing dominance as users turn to conversational AI for direct answers, creative problem solving, and exploratory research.
How should content adapt to how people search now?
Because search engines increasingly present answers before links, content should answer questions directly, use natural language, and include concise definitions and supporting data. This structure aligns with modern search behaviour and improves visibility in both traditional results and AI-driven summaries.