A key debate for content creators is whether Google prioritizes the Published Date vs. Last Updated date when ranking content. This is a common problem because content can become outdated quickly, and a visible date stamp directly impacts user trust and click-through rates. Some websites leave their original publication date untouched, while others refresh their timestamps to appear more relevant. But which approach truly impacts rankings?
At ClickRank, we believe content should be clear, honest, and useful. We’ll dive into the SEO implications of content freshness and how you can optimize your strategy for better visibility. We’ll explore how Google treats these dates, and which one gives you the edge in search results. The final outcome is to help you make an informed decision for your content strategy.
Analyze your domain's health score and fix all issues with a single click.

Why Keeping Your Website Updated Is Essential
Regular updates are crucial for maintaining credibility, user trust, and search engine rankings. A well-maintained website signals professionalism and reliability, much like a clean storefront for a physical business. Actively updating your site is even more important than just knowing how to check a webpage’s last modified date.
1. SEO Benefits
Search engines, particularly Google and Bing, favor regularly updated websites because frequent updates signal relevance and freshness. This leads to better indexing and improved rankings, making it easier for your site to stay visible. For search engines, a website that is regularly maintained is a better resource for users.
To enhance your SEO:
- Regularly refresh keywords to align with current search trends and user intent. This ensures your content remains discoverable for relevant queries.
- Publish new, informative content like blog posts and guides to consistently expand your site’s authority and keyword footprint.
- Revise existing content by updating images, headlines, formatting, and internal links to keep it current.
- Encourage user interactions through comments and reviews, as this can signal to search engines that the content is engaging and valuable.
- Remove or update outdated information to maintain accuracy and prevent users from finding irrelevant details.
2. Relevance and User Experience
If your website looks outdated, visitors may leave quickly, increasing bounce rates and reducing engagement. Keeping your content fresh ensures a better experience and encourages users to return. The user experience is a major ranking factor for Google, so keeping your content up-to-date is a non-negotiable part of good SEO.
To maintain relevance:
- Update high-traffic blog posts with the latest information, statistics, and examples.
- Regularly review product or service pages to reflect current offerings, pricing, or features.
- Ensure contact details, FAQs, and business information are accurate to build trust and prevent frustration.
- Refresh visuals like images, videos, and banners to keep the site engaging and modern.
3. Trust and Credibility
An updated website reassures visitors that your business is active and trustworthy. This is especially important for industries where information changes rapidly.
Ways to boost credibility:
- Keep copyright dates, team member bios, and business details current to show you are an active, professional entity.
- Remove broken links and outdated references that can damage user trust and hurt your site’s SEO.
- Showcase recent testimonials, achievements, or industry updates to highlight your expertise and success.
By consistently updating your website, you enhance user trust, improve SEO performance, and stay ahead of the competition.
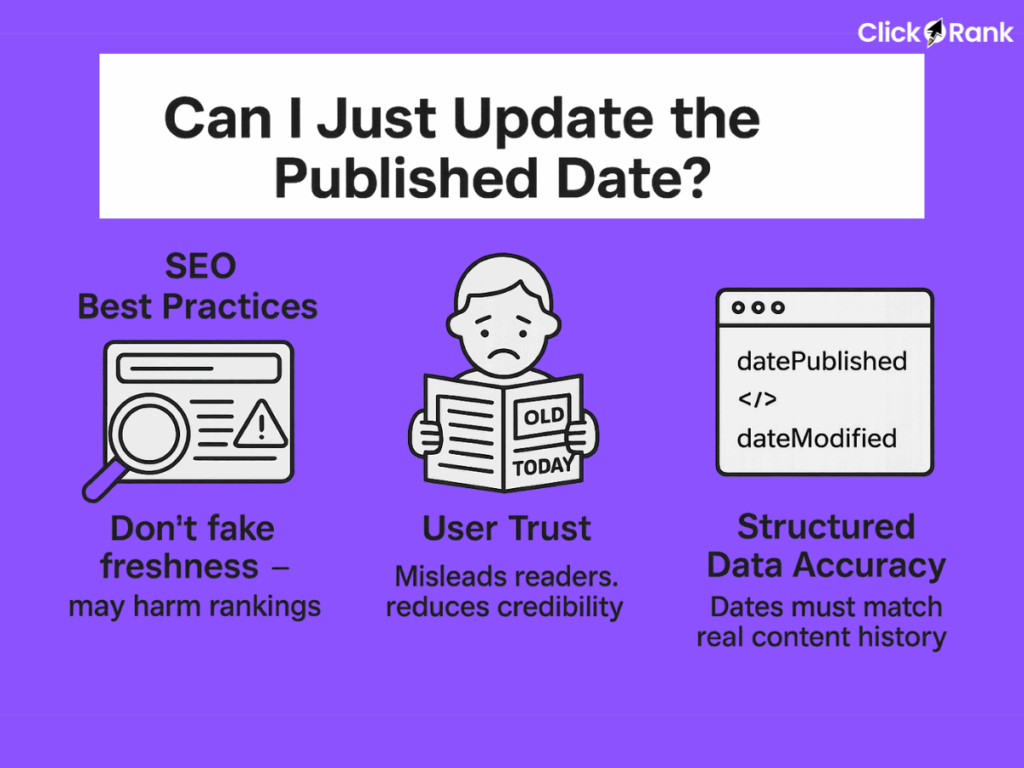
Can I Just Update the Published Date?
No, you should not set the date published as the date updated unless there has actually been a meaningful change to the content. Falsely updating the published date without substantial edits is a deceptive practice that can harm your site in the long run.
Here’s why:
- SEO Best Practices: If you falsely update the date without making significant changes, it may be seen as a form of manipulation and could harm your rankings. Google’s algorithms are designed to detect this type of behavior.
- User Trust: Users are looking for fresh, relevant content. If they click on an article dated today only to find information from five years ago, they will lose trust in your website as a reliable source.
- Structured Data Accuracy: If you’re using schema markup (like Article or BlogPosting schema), ensure
datePublishedanddateModifiedaccurately reflect content history. This schema helps Google understand the true nature of your content.
Best practice: If you make substantial updates (e.g., adding new sections, revising outdated details), then you can and should update the dateModified. However, minor edits like fixing typos or small grammatical tweaks don’t justify changing the date, as they don’t change the substance of the content.
Published Date vs. Last Updated Date: Which One Does Google Show?
When a webpage includes both a published date and a last updated date, website owners often wonder which one Google will display in search results. The reality is that Google does not follow a fixed rule; instead, it decides based on various factors, including the significance of content updates. The search engine’s goal is always to provide the most relevant and timely result to the user.
According to Google’s John Mueller, the company’s approach is flexible, and there is no single rule that determines which date will appear in search results. In a Webmaster Hangout session, he explained:
“In our algorithms, we don’t always pick one or the other as the one that would show. So sometimes we feel that the original date makes sense to show, and sometimes it makes sense to show the last modification date where we know that something significantly changed on this page that affects what the user is looking for.”
This means that if a webpage undergoes significant updates, Google may display the last modified date instead of the original published date to signal freshness. Conversely, if the changes are minor, such as correcting typos or small adjustments, Google might still display the original publication date to show the content’s history. The decision is based on Google’s determination of what is most helpful to the user.
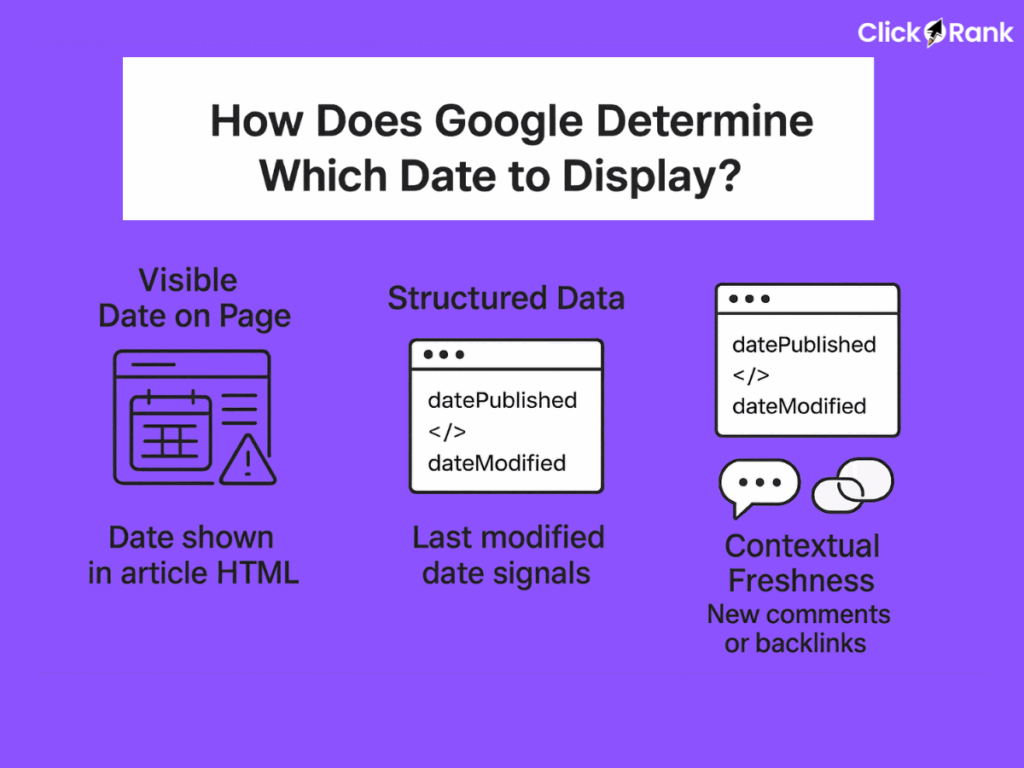
How Does Google Determine Which Date to Display?
Google has a dedicated team focused on identifying and interpreting content dates, yet it is not always accurate. To help Google make the right decision, it’s crucial for you as a content creator to provide clear signals.
Google considers multiple factors when deciding which date to display, including:
- The visible date shown on the webpage: This is the date you display in your HTML, often at the top or bottom of an article.
- The structured data (Schema Markup) that specifies
datePublishedanddateModifiedproperties. This provides a direct, machine-readable signal to search engines. - The last modification date in the page’s HTTP header or sitemap: These are behind-the-scenes signals that also inform Google of changes.
- Other contextual signals that indicate how fresh or relevant the content is, such as new comments or links.
The more consistent and accurate these signals are, the more likely Google will display the date you want it to.
Should You Display Both Dates? The Published Date vs. Last Updated Debate
To maintain transparency and provide the best experience for both users and search engines, it is generally recommended to display both the published date and last updated date on your webpage. This approach offers multiple benefits, serving as a powerful signal of credibility and relevance in the ongoing debate between the Published Date vs. Last Updated dates. It addresses a core need for modern content, which is to be both authoritative and current.
Why Displaying Both Dates is a Best Practice
Displaying both dates is a balanced strategy that satisfies the needs of your audience and search engine algorithms. It shows that your content has a history of authority while also demonstrating your commitment to keeping it accurate and relevant over time.
1. It Improves User Trust
Displaying both dates shows when the content was originally published and when it was last updated. A user can see that while the article may have a long history, it has also been recently reviewed and refreshed. This is particularly valuable for evergreen content, where information may change over time. For example, a comprehensive guide on “Best SEO Practices” published in 2020 might seem outdated, but if it shows a “Last Updated: 2024” date, it reassures the reader that the information is still current and trustworthy. This transparency helps build a stronger relationship with your audience, positioning you as a reliable source.
2. It Helps with SEO and Content Freshness
Google and other search engines rely on dates to understand the freshness of content. A recent “Last Updated” date can be a powerful signal that the information is still relevant, particularly for queries where recency is important (often referred to as “Query Deserves Freshness” or QDF). For evergreen content, this signal helps Google’s algorithms understand that your article is not old or neglected, but rather a consistently maintained resource. By providing both the original publication date and the last updated date, you give search engines clear, non-contradictory signals about the content’s history and its current state.
3. It Encourages Higher Click-Through Rates (CTR)
In search results, users are often more likely to click on a page that looks up-to-date. When a search snippet shows a recent date, it can give your result a significant competitive advantage over other articles that have older, static dates. This higher CTR tells search engines that your content is more appealing and relevant to users, which can lead to better rankings over time. Displaying both dates helps you get the best of both worlds: the authority of a long-standing article combined with the freshness of a recent update.
Best SEO Practices for Handling Content Dates
To optimize how Google processes and displays dates for your pages, consider the following best practices:
- Use Structured Data (Schema Markup): Implement the
datePublishedanddateModifiedproperties in your structured data. This helps Google accurately interpret and display the intended date in a standardized format. - Make the Last Updated Date Visible When Relevant: If an article has undergone major, significant changes, clearly display the last modified date alongside the original publication date. Avoid updating the date for minor edits, as this can be misleading and cause you to lose credibility.
- Ensure Consistency Across Different Signals: The dates displayed in the page content, structured data, and sitemap should all match. Inconsistent dates may confuse Google and result in incorrect date selection in search results.
- Consider the Type of Content: For news articles or time-sensitive content, keeping the original publication date visible may be more important. For evergreen content, highlighting the last updated date can signal freshness and ongoing relevance to users.
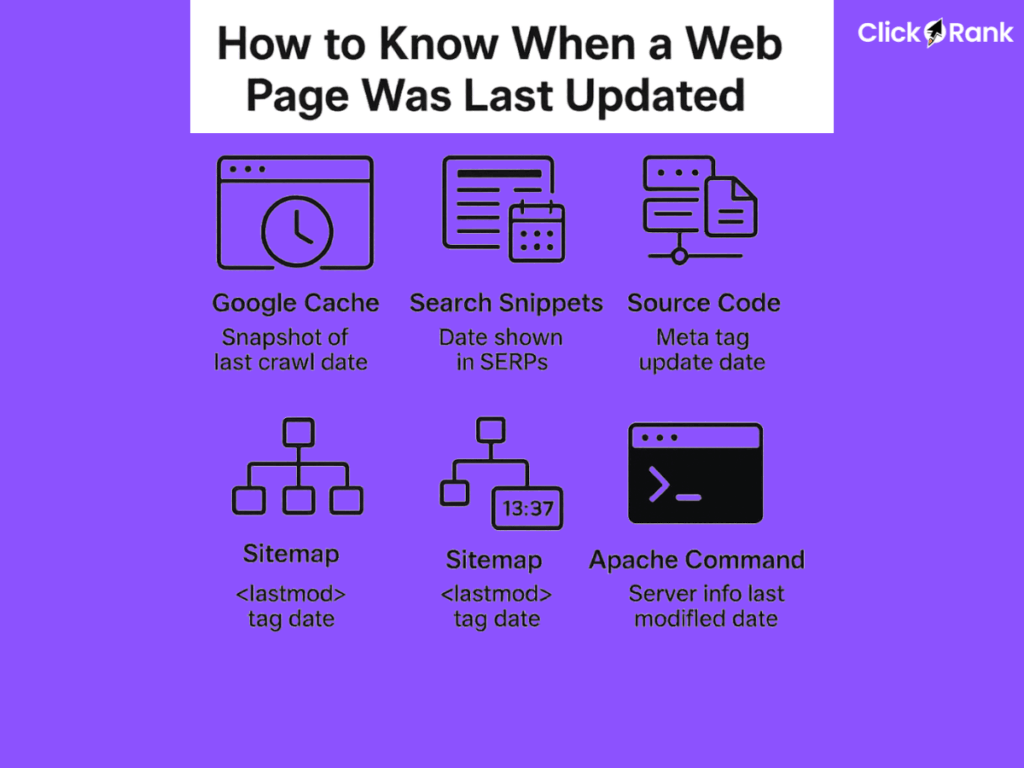
How to Know When a Web Page Was Last Updated
There are several ways to determine the last update date of a web page, each with its own advantages and limitations. Below are different methods you can use to check your own content or a competitor’s.
1. Checking Google Cache for the Last Update Date
Google stores cached versions of web pages, offering a snapshot of the last time the site was indexed. This can be a reliable way to get a recent crawl date.
How to check:
- In your browser, type:
http://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache:http://example.com/(replace “example.com” with the actual URL). - At the top of the cached page, Google will display a message stating when it last captured the page.
2. Using Google Search Snippets
Sometimes, Google displays the last modified date directly in search results. This is often an indicator that Google sees the content as being a recent update.
How to check:
- In the Google search bar, type:
site:www.example.com(replace “example.com” with the actual website). - Look at the snippets under the search results to see if a date appears.
3. Inspecting the HTTP Header for Last Modification Date
Web servers often store information about when a page was last modified in their HTTP headers. This is a technical but accurate method.
How to check:
- Use an online HTTP header checker tool.
- Enter the webpage URL and submit.
- Look for the ‘Last-Modified’ header in the results.
4. Examining the Source Code
Some web pages include metadata that shows when they were last updated. This is a great way to confirm the date a website owner wants search engines to see.
How to check:
- Open the webpage you want to inspect.
- Right-click and select “View Page Source” or “Inspect Element”.
- Press
Ctrl+F(orCommand+Fon Mac) and search for “Last Modified” or “Updated”. - If present, it will appear in a meta tag like:
<meta name="Last-Modified" content="2024-02-15T10:30:00Z" />.
5. Checking the Sitemap for Update Dates
Websites with sitemaps often include timestamps for when each page was last modified. This is another signal for search engines.
How to check:
- Find the website’s sitemap by entering
www.example.com/sitemap.xmlin your browser. - If unavailable, use an online sitemap finder tool to locate it.
- Look for
<lastmod>tags, which indicate the last update date for each page.
6. Using a Command URL (For Apache Servers)
Some Apache-hosted websites allow access to server information, including the last modified date. This is a more obscure but sometimes effective method.
How to check:
- Append
/?=PHPE9568F36-D428-11d2-A769-00AA001ACF42to the website’s URL. - If the website is running Apache, a page may appear displaying the last modified date.
By using these methods, you can determine when a webpage was last updated and ensure you’re accessing the most recent information.
What Dates Are Associated with a Web Page?
When determining how current a web page is, three key dates can offer important insights, and it’s essential to understand the difference between them.
- Published Date: This is the original date when the web page was first created and made publicly available on the internet. It helps users identify when the content was initially written and is a key factor in content authority over time.
- Last Modified Date: This date represents the most recent time the page was updated or its content was altered. It provides a clearer picture of how fresh the information is, especially if the content has undergone significant changes over time. Some websites display this date for transparency, while others do not.
- Indexed Date: This is the date when a search engine, such as Google, last crawled and indexed the page. It indicates when search engines last recognized the page as part of their database, but doesn’t necessarily mean the content was changed on that date.
By examining these dates, users can get a better understanding of a page’s reliability. If all three dates are significantly old, it is likely that the content is outdated and may no longer be relevant. Conversely, if the last modified or indexed date is recent, it suggests that the information has been refreshed and remains useful.
Explore the Full Suite of ClickRank Tools
Now that you understand the importance of content freshness and the debate between Published Date vs. Last Updated, let’s look at how our tools can help you implement these strategies and more. At ClickRank, we believe in providing solutions that make complex SEO tasks fast and simple.
Free AI-Powered SEO Tools
You can access all of these tools from our Free Tools. They are designed to simplify tasks and provide instant support for your content strategy.
- AI Keyword Tool: Generate SEO-friendly keyword suggestions tailored to your content.
- AI Content Idea Generator: Generate blog post, article, or social media content ideas instantly.
- Title Tag Generator: Create optimized title tags for improved SERP visibility.
- Meta Description Generator: Produce compelling meta description copy to increase click-through rates.
- Image Alt Text Generator: Automatically generate descriptive alt text for images to boost accessibility and SEO.
- AI Text Humanizer: Transform AI-generated text into more natural, audience-friendly prose.
Take Control with the ClickRank Platform
In addition to our free tools, the core ClickRank platform automates the hardest parts of SEO, audits, and optimization. It’s a fast, smart SEO solution that helps content teams and digital marketers identify and fix on-page and technical SEO issues in seconds.
- ClickRank Audit: A fast, AI-powered SEO audit that connects to Google Search Console and highlights real issues based on real user data.
- One-Click Fixes: Apply instant fixes to meta tags, headings, links, and more without needing a developer.
- Smart recommendations: Get actionable, prioritized SEO fixes based on actual performance data.
Run a free audit to get started and take control of your SEO without spreadsheets, guesswork, or agency fees.
Final Thoughts
Google may display either the published date or the last updated date, depending on what it determines to be the most relevant for users. Since Google’s date detection is not always accurate, following best practices ensures that your content is properly represented in search results.
By including both dates and using structured data, you provide clear signals to Google while also helping users understand the recency and reliability of your content.

Run your free audit to analyze and optimize your content today.
FAQs
Can I Always Find the Last Update Date on a Webpage?
Not always. While some websites display this information, many do not. In such cases, you can use browser extensions or online tools to uncover the last modification date.
Can I Check Multiple Websites at Once?
Yes, you can. Certain tools allow you to check multiple websites simultaneously, saving time and effort.
How Often Should I Check a Website’s Last Update Date?
It depends on why you need the information. If the content is crucial, frequent checks are recommended. For casual Browse, checking occasionally should be enough.
What If the Last Update Date Isn’t Provided?
You can try various online tools or browser extensions to retrieve this data. However, if no method works, it's best to verify the accuracy of the information before relying on it.
Do Search Engines Track Last Modified Dates?
Yes, search engines like Google track changes on web pages, but they don’t always display the last modified date. Instead, they focus on indexing fresh content based on relevance and updates.



How do I resolve the “Pages with Duplicate Content” error reported by Moz?
You resolve the “Pages with Duplicate Content” error by implementing canonicalization. This involves adding a rel=”canonical” tag to the HTML header of the duplicate pages, pointing the search engine to the single, preferred version of the URL you want indexed. Alternatively, you can merge thin, similar pages into one comprehensive page. This action consolidates link equity and prevents crawl budget waste.
Which specialized tools efficiently generate long-tail keywords for the e-commerce industry?
Specialized tools efficiently generate long-tail keywords for e-commerce by focusing on buyer intent and product variations. Tools like LowFruits and KWFinder by Mangools excel at finding low-competition, longer phrases often missed by broader tools. They leverage Google Autocomplete data to identify specific product searches, review queries, and comparison terms that users type when they are close to making a purchase decision.
What core function does a search algorithm perform for information retrieval?
A search algorithm is a complex system of rules and mathematical formulas used by search engines (like Google) to determine the relevance and ranking of web pages. Its core function is to efficiently process, analyze, and retrieve the most useful and authoritative information from its index in response to a user’s query. The algorithm considers hundreds of ranking factors to provide the best possible list of results to the user.
How does CTR manipulation attempt to influence search engine ranking?
CTR manipulation involves artificially increasing the click-through rate (CTR) of a specific search result by simulating genuine user clicks, often using bots or click farms. The theory suggests that a higher CTR signals to Google that a page is highly relevant, potentially boosting its ranking. However, this is considered a Black Hat SEO technique, carries high risk, and can lead to significant penalties or de-indexing if Google’s algorithms detect the unnatural user behavior.
What specific characteristics define a profitable niche site?
A profitable niche site focuses on a highly specific, narrow topic with dedicated user intent, often targeting low-competition, long-tail keywords. Key characteristics include high topical authority within that segment, a clear monetization path (affiliate marketing, ads), and content designed to answer every possible user query on the subject. The site succeeds by becoming the absolute best resource for that small, profitable audience.
What are the official “Good” thresholds for Core Web Vitals (LCP, CLS, INP)?
The official “Good” thresholds for Core Web Vitals are crucial for a positive user experience and search ranking. Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) must be 2.5 seconds or less. Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) must be 0.1 or less. Finally, Interaction to Next Paint (INP) must be 200 milliseconds or less. Meeting these metrics ensures your website loads quickly, remains visually stable, and responds promptly to user actions.
What tools effectively track organic search ranking?
Tools like Google Search Console ,Ahrefs and clickrank effectively track organic search ranking. These programs show your website’s position for target keywords. They help users see how content performs over time. This valuable data guides your next strategy.
What are some advanced local SEO solutions for businesses?
Advanced local SEO strategies include claiming and optimizing Google Business Profiles, ensuring NAP consistency, using local keywords in content, generating client reviews, and building local citations. Structured data helps Google understand business type and location. Mobile optimization, fast page speed, and internal linking improve local visibility. Tracking local keyword rankings and AI Overview mentions with tools like ClickRank ensures competitiveness. Advanced tactics include geo-targeted content, hyperlocal landing pages, and monitoring competitors for better local positioning, ultimately increasing foot traffic, leads, and conversions.
How does Google handle and what is the impact of duplicate content across multiple, different domains?
Google may index only one version of duplicate content across domains, ignoring others in search results. Duplicate content can dilute rankings, reduce traffic, and harm SEO authority. Use canonical tags, 301 redirects, and noindex directives to indicate the preferred page. Proper attribution and unique content creation help maintain visibility. Regular audits prevent penalties and ensure high-quality indexing.
What are the best free AI-powered tools available for generating image alt text for SEO and accessibility?
Free AI tools include ClickRank Alt Text Generator, Microsoft Azure Cognitive Services, and Canva’s AI alt text feature. They automatically analyze images and generate descriptive alt text for SEO and accessibility compliance. Proper alt text improves user experience, helps visually impaired users, and allows search engines to index images effectively. Reviewing AI-generated text ensures accuracy, relevance, and brand voice. Combining multiple tools helps maintain high-quality, optimized alt text for your website images.
How does SEO work for a one-page website?
One-page websites rely on strategic sections, anchor links, and concise content. Focus on keyword targeting for each section, optimized headings, meta tags, and internal linking via anchors. Tools like ClickRank can monitor rankings and traffic. Mobile-friendliness and fast page speed are critical. Structured data can help highlight key content for search engines. Link-building to the main page enhances authority. Analytics tracking allows adjustments based on engagement metrics. While limited in scope, one-page SEO works by concentrating authority, improving user experience, and ensuring search engines understand the page’s purpose and value.
Où puis-je trouver un générateur de mots-clés gratuit et fiable pour la recherche SEO?
Des outils gratuits fiables incluent Ubersuggest, Keyword Surfer, Google Keyword Planner, et SEMrush (version limitée gratuite). Ils permettent de trouver des mots-clés pertinents, analyser la concurrence, et découvrir des opportunités de contenu. Ces générateurs aident à planifier des campagnes SEO efficaces et à optimiser le contenu pour le classement sur les moteurs de recherche.
What does “not provided” mean for keywords in Google Analytics?
“Not provided” in Google Analytics means Google doesn’t share the search query that brought a user to your website, usually for organic search traffic when users are logged in to Google. This is done to protect user privacy. Although the exact keywords are hidden, tools like ClickRank can track keyword rankings over time, showing which search terms likely bring traffic. Combining Google Search Console data with ClickRank insights helps estimate which pages and keywords are performing. This way, you can optimize content and improve SEO strategy even if Google Analytics doesn’t reveal all keyword data.
como sacar las palabras claves de una investigacion?
Para extraer palabras clave de una investigación, primero analiza el contenido principal, los títulos y subtítulos, y los términos que se repiten con frecuencia. Luego, utiliza herramientas como ClickRank Keyword Generator, SEMrush o Ubersuggest para identificar palabras clave relevantes y de alto volumen de búsqueda. Clasifica las keywords según intención de búsqueda: informativa, comercial o local. Esto ayuda a optimizar artículos, informes o sitios web basados en la investigación. Finalmente, integra estas palabras clave en títulos, meta descripciones y contenido principal para mejorar la visibilidad SEO y atraer tráfico cualificado.
What does a redirect loop mean, and how can I fix it?
A redirect loop occurs when a URL redirects to another URL repeatedly, eventually causing a browser error. This can happen due to misconfigured 301 or 302 redirects, plugin conflicts, or server issues. Redirect loops prevent search engines from indexing content and harm user experience. Tools like Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, or ClickRank can detect loops and broken redirects. Fixing the loop involves correcting redirect rules, consolidating URLs, and ensuring proper canonicalization. Avoiding redirect loops is crucial for maintaining crawlability, preserving SEO value, and ensuring users reach the intended content without errors or delays.
Can marketing automation platforms hurt website SEO potential?
Yes, marketing automation platforms can hurt SEO if improperly configured. Common issues include duplicate content from automated emails, slow-loading landing pages, or incorrect canonical tags. Platforms generating multiple URLs without proper SEO management dilute link equity. Tools like ClickRank can monitor performance and detect issues. To prevent harm, integrate automation with SEO best practices, optimize page speed, and maintain structured data. Properly configured automation enhances lead generation while preserving rankings. Continuous audits and alignment with SEO strategies ensure automation supports growth without negatively impacting organic visibility or website authority.
Are there any reliable cloud-based (online) services that provide tracking for performance within Google’s AI Overviews?
Yes. Tools like seoClarity, SERPWatcher, BrightEdge, and Nozzle are already testing AI Overview (SGE) visibility tracking. These cloud-based tools analyze how often your pages appear in AI-generated results and provide performance metrics. Although SGE tracking is still developing, these platforms are among the first to integrate AI visibility insights into their dashboards.
What is an API (Application Programming Interface) in the context of SEO, and how is it used by marketers?
An API in SEO is a tool that allows data sharing between software systems. For example, marketers use APIs from platforms like ClickRank, Google Search Console, or Ahrefs to collect ranking, keyword, and backlink data automatically. APIs help automate SEO reports, monitor website health, and connect data across dashboards. Instead of manually checking results, marketers can use APIs to pull fresh, accurate insights daily. This saves time, supports scalability, and enables advanced analysis, especially for agencies managing multiple clients or large sites.
What is the PerplexityBot user agent for robots.txt in 2026?
PerplexityBot is an AI-powered search bot. In your robots.txt file, you can control its access by adding User-agent: PerplexityBot followed by Allow: or Disallow: for specific directories. For example, Disallow: /private/ prevents the bot from crawling sensitive pages. Using robots.txt properly ensures your website’s content is indexed as desired. Combining this with ClickRank tracking can help monitor which pages are being crawled and ranked by AI bots. This practice improves SEO control, prevents unwanted indexing, and helps optimize visibility in AI-driven search results in 2026.
Какие показатели SEO мне следует отслеживать?
Для эффективного SEO следует отслеживать такие показатели: позиции по ключевым словам, трафик, CTR, скорость загрузки, Core Web Vitals (LCP, INP, CLS), количество обратных ссылок и индексируемые страницы. Использование инструментов вроде ClickRank позволяет контролировать позиции в поиске и AI Overview, отслеживать конкурентов и анализировать тенденции. Регулярный мониторинг этих метрик помогает улучшать видимость сайта, повышать вовлечённость пользователей и корректировать стратегию SEO.
What does mobile-first indexing mean?
Mobile-first indexing means Google primarily uses the mobile version of your site for indexing and ranking. Since most users browse on mobile devices, your mobile layout, speed, and content quality are now critical for SEO. Websites that are mobile-friendly tend to rank higher, while desktop-only designs may lose visibility. Tools like Google Search Console can check mobile usability. Optimizing for mobile improves user experience, reduces bounce rates, and ensures your content is fully visible and indexed correctly by Google, aligning with modern SEO best practices.