You’ve poured time and effort into your website, crafting compelling content, optimizing landing pages, and building a strong online presence. But what happens when a page simply vanishes? A visitor clicks a link, and instead of finding the information they sought, they’re met with the cold, uninviting message: “404 Not Found.” It’s an unwelcome and frustrating dead end.
Here’s the thing: 404 errors are a normal, unavoidable part of a website’s lifecycle. Pages get moved, content becomes outdated, and URLs change. The problem isn’t the existence of 404s; it’s how you mishandle them. A poorly managed 404 strategy can cost websites up to 30% of their organic traffic. You can’t let valuable link equity, hard-earned user trust, and potential conversions simply disappear.
This guide will demystify the process of handling 404 errors. You’ll learn what they are, why they happen, and the right way to fix them so you don’t lose traffic or valuable backlinks.
Analyze your domain's health score and fix all issues with a single click.

What Is a 404 Error Redirect?
A 404 error redirect is a technique used to send visitors and search engines from a broken, non-existent page to a new, relevant page. This process is crucial for maintaining a good user experience and preserving SEO value.
- 404 Status vs. Redirect: A 404 status code is a standard HTTP response that tells browsers and search engines the requested resource could not be found. This means the client was able to communicate with the server, but the server couldn’t locate the specific URL. A redirect, on the other hand, is an instruction that actively sends a browser from one URL to another. A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect that informs search engines that a page has been permanently moved, transferring its SEO value to the new URL.
- When to Redirect: A redirect is the correct course of action when a page has been permanently moved, the content has been updated and a new URL was created, or if you have a highly relevant alternative for your users. Redirecting a broken link to a new page with relevant content is a recommended best practice.
- When Not to Redirect: If a page is permanently gone and there is no suitable replacement, it is often best to leave it as a 404 or, better yet, use a 410 status code to signal permanent removal.
Why 404 Errors Happen (And Why That’s Normal)
You might be surprised to learn that 404 errors are an inevitable part of maintaining a healthy website. They are not necessarily a sign of a technical flaw but rather a normal byproduct of a dynamic web presence. They occur for a variety of reasons, many of which are completely outside of your control.
Common Causes:
- Deleted pages or products: When content or products are removed from your site, the URL that once led to them will return a 404 error.
- Changes to URLs without redirects: If you change a page’s URL (e.g., changing the permalink) and fail to implement a redirect, the old URL will lead to a 404.
- Typographical errors in links: A simple typo in an internal or external link can lead users to a non-existent page.
- Broken inbound links from other websites: Other websites may link to a page on your site that no longer exists, creating an external broken link.
- Outdated parameters or filters on a page: In some cases, dynamic URLs with old query parameters may lead to a 404 error.
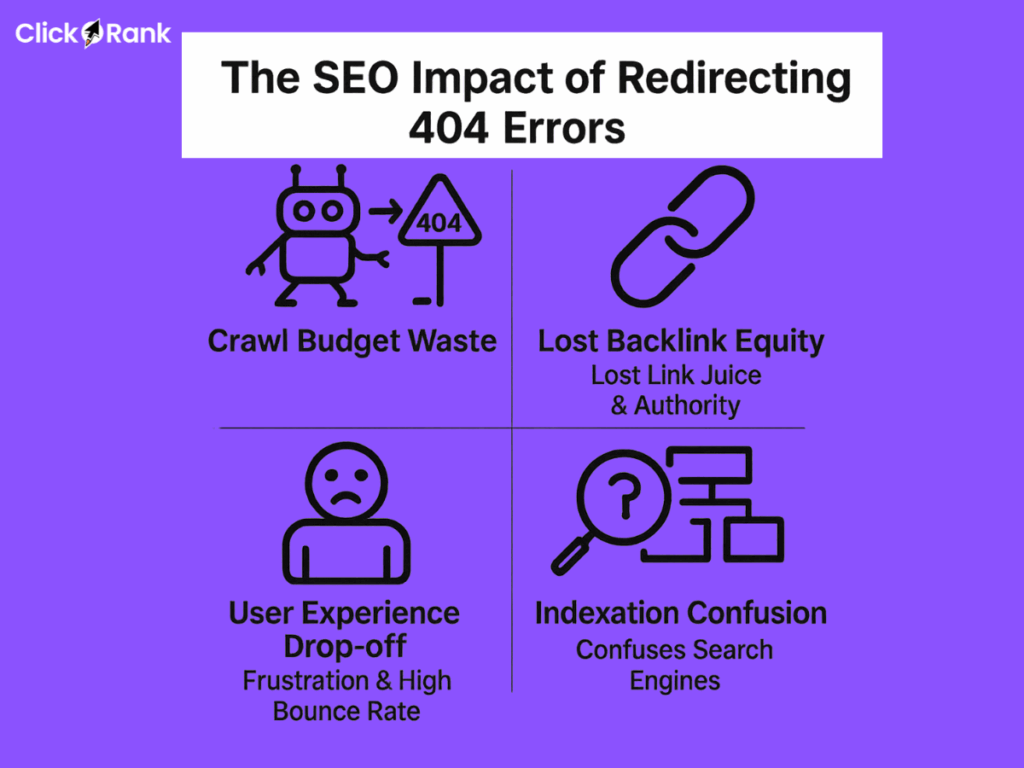
The SEO Impact of Redirecting 404 Errors
Properly managing 404 errors is critical for a number of technical SEO reasons. When you fail to address them, you risk a number of negative consequences that can hamper your site’s performance.
Crawl Budget Waste
Search engines like Google use web crawlers to discover and index pages. A crawl budget is the number of pages a search engine is willing to crawl on your site within a specific timeframe. When a crawler encounters a 404 error, it hits a dead end, wasting valuable crawl budget on a non-existent page instead of discovering and indexing your important content. This can lead to delayed indexing of new pages and updates. Googlebot may revisit a persistent 404 page up to 20 times before stopping.
Lost Backlink Equity
Backlink equity, or “link juice,” is the authority a page passes on to others via links. When a page with valuable backlinks returns a 404 error, that link equity is lost. You’re essentially throwing away the ranking power and referral traffic those links provide.
User Experience Drop-off
A 404 page is a frustrating experience for users. When they land on a dead end, they are likely to leave your site quickly, which increases your bounce rate. A high bounce rate signals to search engines that users are not finding what they are looking for, which can negatively impact your rankings.
Indexation Confusion
While Google states that 404 errors don’t directly hurt your site’s overall ranking, an excessive number of them can be a sign of a neglected or low-quality website. This can negatively impact how your content is ranked, even if the content itself is high-quality.
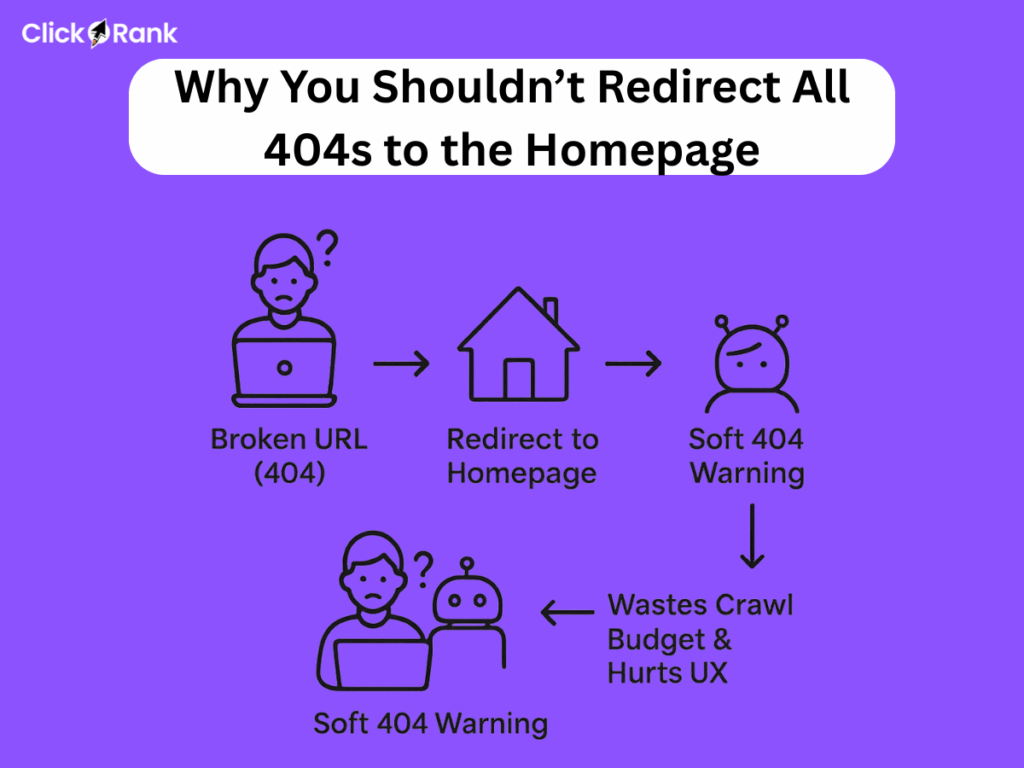
Why You Shouldn’t Redirect All 404s to the Homepage
A common misconception is that redirecting all 404 errors to the homepage is a good way to “fix” the problem and retain traffic. However, this is a harmful and antiquated practice.
Here’s what Google’s Martin Splitt has to say:
“A 404 is a very clear signal this link is wrong and broken or this URL no longer exists because maybe the product doesn’t exist or something has changed.”
Confusion for Crawlers and Users:
Redirecting all non-existent pages to the homepage creates what is known as a “soft 404.” A soft 404 is a URL that returns a 200 “OK” status code but is essentially an error page with very little content. It misleads both users and search engine crawlers. A user expecting a specific page lands on a generic homepage with no context, leading to a poor experience and a likely immediate bounce. For crawlers, it makes it difficult to differentiate between valid pages and broken ones, leading to wasted crawl budget.
Best Practices for Handling 404 Errors
Managing 404 errors is a nuanced process that requires a strategic approach. Here are the key best practices you should follow to handle them correctly.
- Create a Custom 404 Page: Instead of a generic browser-generated error page, you should design a custom 404 page that is on-brand and helpful. This page should clearly state that the requested page was not found, but it should also provide users with helpful alternatives, such as a search bar, a link to your homepage, or links to your most popular content. A well-designed custom 404 page can reduce bounce rates by up to 20%.
- Use Targeted 301 Redirects: Only implement a 301 redirect if you have a new URL that is highly relevant to the old one. The purpose of the redirect is to seamlessly send users and search engines to the most logical replacement for the missing content.
- Avoid Blanket Redirects: As mentioned, never redirect all 404s to the homepage or a top-level category page. This practice is detrimental to both user experience and SEO.
- Monitor 404s Regularly: You should have a process in place to regularly check for new 404 errors on your site. You can use tools like Google Search Console to keep an eye on new errors.
- Use 410 for Permanently Removed Content: The 410 “Gone” status code tells search engines that the page has been intentionally and permanently removed and is not coming back. A 410 signal can speed up the de-indexing of content faster than a 404 does.
How to Redirect 404 Errors Without Hurting SEO
Fixing 404s doesn’t have to be a daunting task. By following a simple, step-by-step process, you can handle them efficiently and correctly.
Step 1: Identify 404 pages
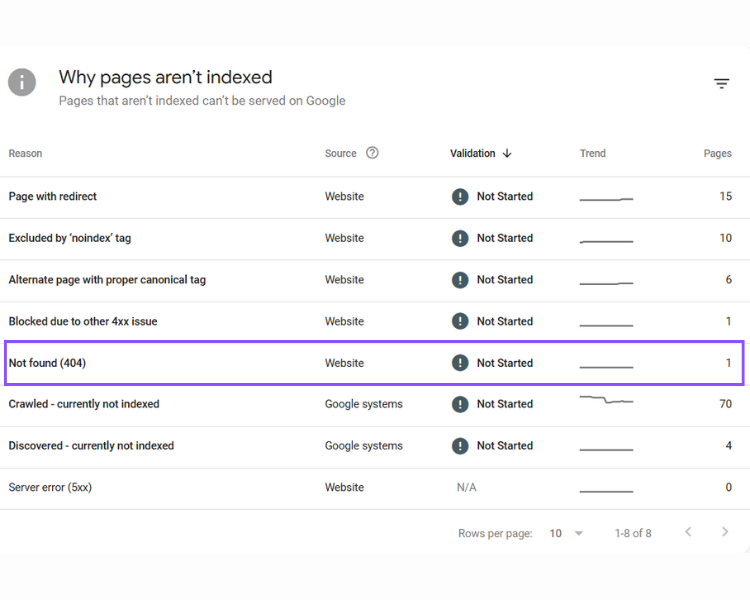
Before you can fix them, you need to find them. The best way to do this is with a website crawler or an analytics tool. Google Search Console (GSC) is a fantastic free option that will show you all the 404 errors Google has discovered on your site. Other tools like Screaming Frog and Ahrefs can also help you find broken links.
Want to Climb Google Faster? Find the top rank tracking tools that get real results.
Step 2: Decide what to do
For each error, you need to decide on the best course of action.
- If a new version of the content exists, you should redirect the old URL to the new one.
- If the page was deleted and there is no relevant replacement, you can either leave it as a 404 or set a 410 status code.
- If the URL has valuable backlinks, you should prioritize redirecting it to the most relevant page possible to preserve that link equity.
Step 3: Implement the redirect
The method you use will depend on your website’s platform. For WordPress sites, a plugin is often the easiest route. For server-side redirects, you may need to edit files like .htaccess (for Apache) or a configuration file (for Nginx).
Step 4: Test it
After you implement a redirect, it’s crucial to test it to ensure it’s working correctly. Simply copy the old URL into your browser and make sure it automatically takes you to the new, intended destination.
Step 5: Monitor the results
After implementing your redirects, check a tool like GSC to ensure the errors are no longer being reported and that traffic is successfully flowing to the new pages.
Platform-Specific Redirect Methods
The technical process for implementing redirects can vary depending on your website’s platform. Here’s a quick overview of how you can handle redirects on some of the most common systems.
| Platform | Method | Tools/Plugins | Notes |
| WordPress | 301 Redirect Plugin | Redirection, RankMath | Plugins are the easiest way to manage redirects, but be careful to avoid homepage loops. |
| Shopify | URL Redirects | Built-in tool | Shopify has a built-in tool for creating redirects. It’s a simple, manual process. Note that it cannot redirect dynamic search URLs. |
| Apache | .htaccess rules | N/A | This method requires FTP access to your server. It’s powerful but can be risky if not done correctly. |
| Nginx | Config file edit | N/A | Requires you to edit your server’s configuration file and may require a server restart to take effect. |

Key Facts for Your 404 Strategy
Let’s dispel some common myths and reinforce some key facts to help you develop a robust 404 strategy.
Google doesn’t penalize sites for occasional 404s.
They are a normal part of the web. The problem is not the existence of a few 404s, but a pattern of neglect or an overwhelming number of them.
A 301 redirect passes most link equity, but not all of it.
While it’s the best way to preserve link value, there is a small amount of equity lost in the redirect process.
A 410 status code helps speed up the de-indexing of content.
Use it when you are certain a page is gone forever and you want search engines to remove it from their index quickly.
A custom 404 page can reduce bounce rates by up to 20%.
It’s a powerful tool for user retention and can turn a negative experience into a positive one.
How ClickRank Helps You Manage 404s
Managing 404s can be a lot of work, but our platform makes it easier. ClickRank is a fast, smart solution that helps content teams take control of SEO. We automate the hardest part of SEO, audits and optimization, so our users can focus on what actually drives growth: content, strategy, and visibility.
- Automated 404 detection: Our AI-powered SEO audit connects to Google Search Console and highlights real issues based on real user data, so you always know when a new 404 appears.
- Smart redirect suggestions: We give you actionable, prioritized SEO fixes based on actual performance data.
- Backlink reclamation reports: Our platform helps you see where you’re losing valuable link equity, so you can fix it fast.
You can run a free audit and apply instant fixes to meta tags, headings, links, and more without needing a developer. We help content teams take control of SEO, without spreadsheets, guesswork, or agency fees.

Ready to take control of your SEO? Run a free audit today!
Final Thoughts
Don’t fear 404s they’re a normal part of running a website. The key is to manage them smartly and proactively. With the right strategy, you can turn a potential negative into a positive by improving your user experience and preserving your hard-earned SEO value. Let ClickRank be your trusted partner in that journey.
FAQs
Do 404 errors hurt SEO?
No, Google doesn't penalize a website for occasional 404 errors . The issue arises from a poorly managed 404 strategy, which can waste your crawl budget and lead to a bad user experience. A large number of unaddressed 404s can signal a neglected site, which may indirectly impact your site's overall quality and visibility.
Should I redirect all 404 errors to the homepage?
Warning: Undefined array key "answer" in /home/clickrank/htdocs/www.clickrank.ai/wp-content/plugins/structured-content/templates/shortcodes/multi-faq.php on line 20
Deprecated: str_contains(): Passing null to parameter #1 ($haystack) of type string is deprecated in /home/clickrank/htdocs/www.clickrank.ai/wp-includes/shortcodes.php on line 246
Deprecated: htmlspecialchars_decode(): Passing null to parameter #1 ($string) of type string is deprecated in /home/clickrank/htdocs/www.clickrank.ai/wp-content/plugins/structured-content/templates/shortcodes/multi-faq.php on line 20
When should I use 301 vs. 404 vs. 410 status codes?
301 Redirect: Use a 301 redirect when a page has been permanently moved to a new, relevant URL. This is the best way to preserve most of the page's SEO value. 404 Not Found: Use a 404 status code for temporary errors or when a page doesn't exist and there is no suitable replacement. 410 Gone: Use a 410 status code when a page has been intentionally and permanently removed. This tells search engines to de-index the page faster than a 404.
How do I find 404 errors on my website?
You can find 404 errors on your website using various tools. Google Search Console (GSC) is the most common free tool for this purpose. You can also use other website crawling tools to identify broken links and pages.
Can you redirect a 404 error?
Yes, you can and should redirect a 404 error, but only when a relevant replacement page exists . This practice helps maintain a good user experience and preserve valuable backlink equity.
How do I reclaim backlinks from 404 pages?
To reclaim backlinks from 404 pages, you should identify pages with inbound links that are returning a 404 error and implement a targeted 301 redirect from the broken URL to the most relevant live page on your site . This action transfers the link equity to the new page, preventing its loss.