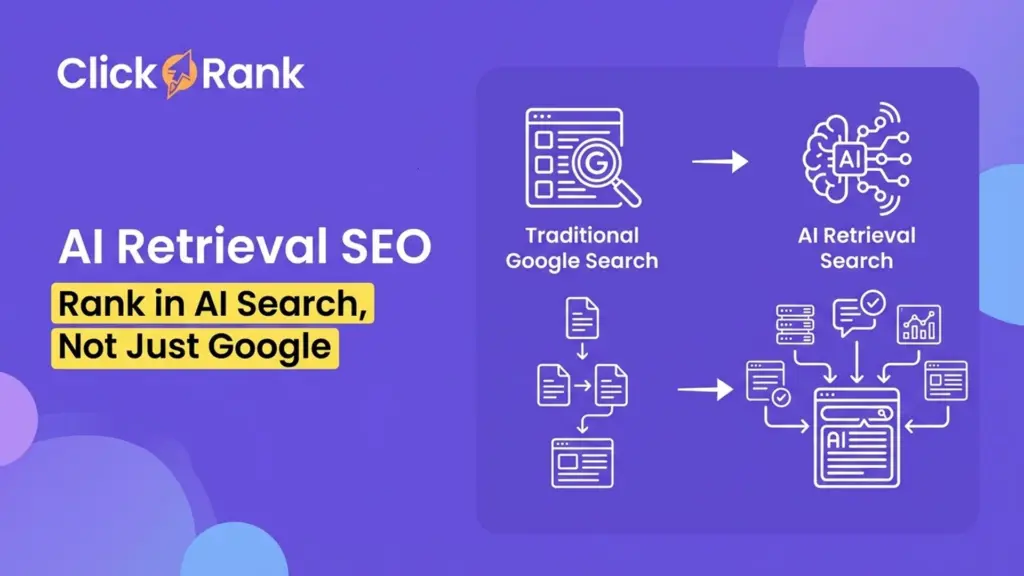
Structured Data Stacking solves one clear problem: AI search engines struggle to trust and reuse content that lacks strong, connected schema signals. In 2026, ranking alone is not enough. AI systems like answer engines and generative search need structured context to decide which sources are reliable enough to cite. This is where Structured Data Stacking becomes critical.
This topic matters because most websites still use basic, single-layer schema that only validates content but does not explain relationships. AI-driven search favors pages that clearly define entities, ownership, intent, and hierarchy. Without stacked schema, even high-quality content can be ignored by AI answers.
What Is Structured Data Stacking and Why Does It Matter for AI Search?
Structured Data Stacking is a layered schema strategy that helps AI search engines clearly understand your content, entities, and context. Instead of using one basic schema, you stack multiple connected schema types to reinforce meaning. This matters because AI search in 2026 relies more on structured signals than rankings alone. Search engines and AI models now extract answers, not just links, and schema helps them trust what your page represents.
For SEO and AEO, this approach improves eligibility for AI answers, citations, and rich results. Basic schema often sends weak or incomplete signals, which AI may ignore. Structured Data Stacking solves this by building clarity across entities, content types, and relationships. The practical benefit is simple: higher AI visibility, stronger trust signals, and better chances of being selected as an answer source instead of just another result.
What is structured data stacking in modern SEO?
Structured data stacking is the practice of layering multiple related schema types to describe a page more completely. Instead of adding only Article or FAQ schema, you connect Organization, WebPage, Article, FAQ, and entity references together. This gives AI systems a full context, not fragments.
In modern SEO, this matters because AI engines do not guess intent well from raw text alone. They rely on structured relationships. A single schema explains one thing. A stacked schema explains how everything connects. For example, an article linked to a verified organization and author entity carries more trust.
Basic schema setups fail because they are isolated. Stacking turns schema into a system. The result is stronger eligibility for AI summaries, featured answers, and citations across AI-driven search platforms.
How is structured data stacking different from traditional schema markup?
Structured data stacking goes beyond traditional schema by focusing on relationships, not just validation. Traditional schema markup aims to qualify for rich results. Stacking aims to build entity clarity for AI systems.
Old approaches treat schema as a checkbox. Add one schema, test it, and move on. Stacking treats schema as architecture. Each schema supports another using shared entities, @id links, and consistent references.
This difference matters because AI models evaluate trust across signals. A layered schema strategy reduces ambiguity and reinforces meaning. Traditional schema may still pass tests, but it often fails to influence AI answers. Structured Data Stacking aligns schema with how AI systems actually read, connect, and trust information.
Is it safe to use multiple schema types on one page?
Yes, it is safe to use multiple schema types on one page when they accurately represent the content. Google and AI systems expect complex pages to have layered meaning. An article page can also be a webpage, part of a website, published by an organization, and contain FAQs. Using multiple schema types reflects reality, not manipulation.
Problems only arise when schema is misleading or unrelated. For example, adding Product schema to an informational blog post creates confusion. Safe stacking follows content truth. Each schema should support what users actually see. When done correctly, multiple schemas strengthen clarity and reduce misinterpretation by AI systems.
How do Google and AI models interpret overlapping schemas?
AI models interpret overlapping schemas by looking at shared entities and relationships, not by counting schema blocks. They resolve meaning through @id links, sameAs references, and consistent entity names. Overlap is not a conflict if schemas describe different layers of the same content.
Google and AI systems merge these signals into one understanding. If schemas contradict each other, trust drops. If they align, confidence increases. Overlapping schema works best when each layer adds detail without changing meaning. This is why structured data stacking must be planned, not randomly added.
How do AI search engines read and interpret structured data?
AI search engines read structured data as verified context, not decoration. Schema tells AI what a page is about, who created it, and how entities relate. This helps models reduce guesswork and extract accurate answers.
Unlike traditional crawlers, AI systems prioritize meaning over keywords. Structured data acts as a guide map. It clarifies intent, relationships, and authority signals. When schema is missing or weak, AI relies on assumptions, which lowers selection chances.
Structured Data Stacking improves interpretation by reinforcing the same entities across layers. This makes it easier for AI to trust, summarize, and cite your content in direct answers and AI-generated responses.
Why do AI models prioritize entities over keywords?
AI models prioritize entities because entities represent real-world concepts with stable meaning. Keywords change by context, language, and phrasing. Entities do not. A person, brand, or topic entity remains consistent across pages and platforms.
Entities allow AI to connect information across sources. When schema defines entities clearly, AI can verify accuracy faster. Keyword-heavy pages without entity signals often get ignored. Entity-first understanding is more reliable for AI answers, citations, and summaries.
How does schema act as “ground truth” for AI answers?
Schema acts as ground truth by explicitly stating facts that AI would otherwise infer. It confirms who the author is, what the topic represents, and how content fits into a larger knowledge graph. This reduces ambiguity.
When AI generates answers, it prefers sources with clear, machine-readable facts. Structured data provides that certainty. In stacked form, schema repeats and reinforces truth across layers. This makes your content easier to trust, extract, and reuse in AI-driven search results.
How AI Search Engines Actually Use Structured Data
AI search engines use structured data as a confidence layer to generate answers, summaries, and citations. Instead of relying only on page text, AI systems scan schema to understand meaning, relationships, and trust signals. This shift matters because AI-driven search focuses on answer quality, not ranking position. Structured data helps AI decide what your content represents and why it should be trusted.
In 2026, AI engines use schema to speed up understanding and reduce errors. Pages with clear, layered schema are easier to parse and more likely to be selected for zero-click answers. Without structured data, AI must infer intent, which lowers accuracy and visibility. The practical benefit is strong: structured data increases your chances of being quoted, summarized, or cited directly by AI search tools instead of being skipped.
How does Google SGE use structured data to generate answers?
Google SGE uses structured data to validate facts, entities, and content type before generating answers. Schema helps SGE confirm whether a page is informational, authoritative, and relevant to the query. This reduces hallucinations and improves answer accuracy.
SGE combines schema with on-page content, but structured data acts as a shortcut. It highlights key details like authorship, topic focus, and relationships. Pages with stacked schema provide clearer signals, making them easier for SGE to summarize confidently. Without schema, even good content may be overlooked. The best practice is to align schema closely with page intent so SGE can extract clean, reliable answers.
Does SGE directly extract answers from schema markup?
SGE does not always extract full answers directly from schema, but it uses schema to validate and frame answers. Schema confirms facts like definitions, entities, and relationships. This helps SGE trust the surrounding content when generating responses.
For example, FAQ schema may guide answer structure, while Article schema confirms topic relevance. Schema rarely replaces content, but it strengthens it. When schema and content align, SGE can generate answers faster and with higher confidence. This is why schema accuracy matters more than volume.
Which schema types are most influential for SGE visibility?
The most influential schema types for SGE include Organization, Article, FAQ, and WebPage. These help define authority, topic scope, and answer-ready content. Breadcrumb schema also helps with context and hierarchy.
SGE favors schemas that clarify intent and credibility. Product or Review schema matters for transactional queries, while FAQ schema supports question-based answers. Stacking these schemas correctly increases visibility by giving SGE multiple trust signals pointing to the same meaning.
How do ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Bing AI use schema data?
ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Bing AI use schema data to understand context, verify entities, and choose citation-worthy sources. Schema helps these systems identify reliable pages faster, especially when generating answers across multiple sources.
These platforms rely on structured signals to reduce ambiguity. When schema clearly defines authors, organizations, and topics, AI systems can map content into their knowledge frameworks. This improves citation accuracy and reduces misattribution. Pages without schema may still be read, but they compete at a disadvantage. Structured Data Stacking improves consistency across AI platforms, not just one engine.
Why is structured data critical for AI citations and sourcing?
Structured data is critical because AI systems need clear signals to assign credit and citations. Schema defines who published the content and what it represents. This helps AI avoid unreliable or unclear sources.
When entities are well-defined, AI can safely reference them in answers. Without schema, AI may summarize content without attribution or ignore it entirely. Structured data increases both visibility and brand recall in AI-generated responses.
Do AI models trust JSON-LD more than on-page HTML content?
AI models generally trust JSON-LD more because it is explicit and machine-readable. HTML content requires interpretation, while JSON-LD states facts directly. This reduces errors and speeds up processing.
That said, AI compares JSON-LD with visible content. If they mismatch, trust drops. The best results come when JSON-LD accurately reflects the page. Clean, consistent JSON-LD supports stronger AI understanding and citation confidence.
How has the role of structured data changed from SEO to AEO?
Structured data has shifted from enhancing snippets to powering answers. In traditional SEO, schema helped improve appearance. In AEO, it helps determine whether your content becomes the answer.
AI systems now prioritize clarity, trust, and entity context. Structured data provides all three. This change means schema is no longer optional or cosmetic. It is foundational for AI visibility. Brands that adapt gain exposure even without clicks, while others lose relevance in answer-based search.
Why keyword-based optimization is losing relevance?
Keyword-based optimization is losing relevance because AI understands meaning, not repetition. AI models can interpret synonyms and context without exact matches. Keywords alone do not establish trust or authority.
Schema and entities provide stronger signals than keyword density. Pages optimized only for keywords often lack clarity for AI systems. This leads to lower selection rates for AI answers and summaries.
How structured data supports Answer Engine Optimization (AEO)?
Structured data supports AEO by making content easy to extract, verify, and reuse. Schema defines question-answer structures, entities, and credibility signals. This aligns perfectly with how answer engines work.
When schema is stacked correctly, AI can confidently surface your content as a direct answer. This boosts zero-click visibility, citations, and long-term brand authority across AI-driven search platforms.
Entity-First SEO
Entity-first SEO is an optimization approach that focuses on clearly defined entities instead of keywords. AI systems rely on entities because they represent real people, brands, places, and topics with stable meaning. In AI-driven search, entities help models connect information across sources and verify accuracy faster. This matters in 2026 because AI answers are built from trusted knowledge graphs, not keyword matches.
When your content is entity-first, AI understands who you are, what you cover, and how you relate to a topic. Structured data stacking strengthens this by explicitly defining entities and their relationships. The practical benefit is higher AI trust, better citation chances, and stronger visibility in zero-click answers. Keyword-only pages often get ignored, while entity-rich pages become reference points for AI systems.
What are entities and why do AI systems rely on them?
Entities are clearly defined concepts such as people, organizations, products, or topics that exist independently of wording. AI systems rely on entities because they remove ambiguity. Different words can describe the same idea, but an entity always points to one meaning.
For AI search, entities are easier to verify and connect. They allow models to build knowledge graphs and cross-check facts. When your content defines entities clearly, AI can place it accurately within its understanding of the web. This improves trust and relevance. Pages without clear entity signals force AI to guess, which reduces selection chances. Entity-first optimization ensures your content fits cleanly into AI-driven answer systems.
Difference between people, organizations, and topic entities
People entities represent individuals with identities, roles, and expertise. Organization entities represent brands, companies, or publishers with authority and history. Topic entities represent subjects or concepts, such as “structured data stacking” or “entity SEO.” Each type serves a different purpose for AI understanding.
AI uses people entities to assess expertise, organizations to assess trust, and topic entities to understand relevance. Mixing these correctly helps AI evaluate credibility. For example, an article written by a person entity and published by an organization entity about a topic entity sends strong trust signals when all are consistent.
How AI uses entities to build knowledge graphs
AI uses entities as nodes in knowledge graphs. Each entity connects to others through relationships like authorship, publication, or topical relevance. Structured data helps define these links clearly.
When entities are well-defined, AI can reuse information across answers. This makes your content more likely to be cited repeatedly. Poor entity signals result in weak or missing connections, reducing long-term AI visibility.
How does structured data create entity relationships?
Structured data creates entity relationships by explicitly linking entities using properties like @id, sameAs, author, and publisher. These links tell AI how entities relate across pages and domains.
Instead of isolated content, schema turns pages into connected data points. This helps AI confirm identity and consistency. Entity relationships also reduce confusion between similar names or topics. Strong relationships improve trust and increase chances of being selected for AI answers. Without structured data, these relationships remain implicit and weaker.
Using @id, sameAs, and entity references correctly
The @id property creates a unique identifier for an entity. sameAs links that entity to trusted external profiles. Together, they help AI confirm identity across sources.
Correct usage requires consistency. The same @id should be reused across pages. sameAs links should point to authoritative profiles only. This clarity strengthens AI confidence and reduces misidentification.
How consistent entity signals improve AI trust
Consistency across schema, content, and site-wide signals builds trust. When entity names, descriptions, and references match everywhere, AI confidence increases.
Inconsistent signals confuse AI and weaken authority. Consistent entity stacking makes your brand and topics easier to recognize, remember, and cite in AI-generated answers.
Why entity stacking outperforms keyword optimization
Entity stacking outperforms keyword optimization because AI evaluates meaning, not repetition. Entities provide context, relationships, and trust signals that keywords cannot.
Keyword-focused pages may rank briefly, but entity-rich pages become long-term references. Entity stacking supports durable AI visibility. It also aligns with how AI systems retrieve and reuse information across multiple answers and platforms.
Why AI ignores keyword density signals
AI ignores keyword density because it understands language semantically. Repeating words does not add meaning or trust. In some cases, it reduces credibility.Instead, AI looks for clear entity definitions and relationships. Pages relying on keyword tricks fail to provide structured understanding, lowering selection chances.
How entity depth improves AI visibility and citations
Entity depth means covering an entity fully, including its attributes, relationships, and context. This helps AI understand the topic beyond surface level.Deeper entity coverage increases citation frequency and improves visibility in AI answers. AI prefers sources that fully explain entities, not just mention them.
Structured Data Stacking Architecture
Structured data stacking architecture is the planned structure of how multiple schema types work together on a page and across a site. Instead of adding schema randomly, you build a clear hierarchy that mirrors how AI understands content. This matters because AI systems look for order, consistency, and relationships. A strong architecture helps AI quickly identify entities, page purpose, and authority signals.
In 2026, AI-first search favors sites with clean schema structure over sites with scattered markup. A proper stacking architecture reduces confusion and improves AI trust. The practical benefit is higher eligibility for AI answers, better citations, and more consistent interpretation across platforms. Without architecture, even valid schema can send mixed signals that weaken visibility.
What does an ideal structured data stack look like on a page?
An ideal structured data stack clearly defines who owns the content, what the site represents, and what the specific page delivers. It starts with Organization and Website schema, then connects to WebPage and content-specific schemas like Article or FAQ. All layers share consistent entity references.
This structure matters because AI systems process schema top-down. When ownership and context are clear, page-level schema becomes more trustworthy. Stacked schema should feel connected, not duplicated. Each layer adds meaning. The result is faster AI understanding and stronger confidence when generating answers or citations.
Organization → Website → WebPage hierarchy explained
This hierarchy mirrors how AI understands digital content. The Organization schema defines the brand entity. Website schema explains the digital property. WebPage schema describes the individual page.
When these are linked with shared @id values, AI can trace content ownership and context easily. This reduces ambiguity and improves authority signals. Breaking this hierarchy often leads to weak or ignored schema signals.
Article → FAQ → Breadcrumb schema layering strategy
Article schema defines the main content. FAQ schema highlights question-based answers. Breadcrumb schema explains page position within the site.
Layering these together helps AI understand both content depth and structure. This improves answer extraction and contextual relevance. Each schema supports a different AI need without overlap or conflict.
How do you apply schema stacking across topic clusters?
Schema stacking across topic clusters connects related content through shared entities and references. Pillar pages and cluster articles should reference the same Organization, author, and topic entities.
This approach helps AI recognize topical authority across multiple URLs. It also strengthens internal knowledge graph signals. The practical benefit is improved AI recall across related queries, not just one page.
Connecting pillar pages and supporting content via schema
Pillar and cluster pages should share consistent entity IDs. Article and About properties can reference the same topic entity.This creates a visible relationship between pages. AI can then treat the cluster as a unified knowledge source instead of isolated posts.
Reinforcing the same entity across multiple URLs
Reusing the same @id across pages confirms entity consistency. AI recognizes this as the same brand or topic appearing repeatedly.This repetition builds trust over time. It also increases the likelihood of being cited across multiple AI answers.
What is the difference between page-level and site-wide schema?
Page-level schema describes what a specific page contains. Site-wide schema defines global entities like organization, website, and publisher.
Understanding this difference prevents misuse. Site-wide schema builds baseline trust. Page-level schema delivers relevance. Both are required for effective structured data stacking.
Which schema types should always be site-wide?
Organization, Website, and Publisher schema should always be site-wide. These define ownership and authority.They provide a stable foundation for AI interpretation across the entire site.
Which schema should only be used on specific pages?
Article, FAQ, Product, and HowTo schema should only appear where relevant. Using them site-wide creates confusion.Targeted usage keeps signals clean and improves AI understanding.
Priority Schema Types for AI & AEO
Priority schema types are the schema formats that most strongly influence AI trust, answer selection, and citations. Not all schema types matter equally for AI-driven search. In 2026, AI systems prioritize schema that clearly defines authority, intent, and answer-ready content. Using the right schema types in a stacked way helps AI engines quickly assess whether your content is reliable enough to be used as a source.
For AEO, the focus shifts from visual enhancements to meaning and credibility. Organization, Article, FAQ, and intent-mapped schemas play a central role. When these schemas are stacked correctly, AI can understand who you are, what the content explains, and how it should be used in answers. The practical benefit is stronger AI visibility, better citations, and higher zero-click exposure across answer engines.
Why is Organization schema critical for AI trust?
Organization schema is critical because it defines the primary trust entity behind your content. AI systems want to know who is responsible for the information before using it in answers. Organization schema provides that clarity.
This schema helps AI assess brand legitimacy, topical focus, and authority signals. When linked with Website, Article, and author entities, it creates a clear trust chain. Without Organization schema, content often appears anonymous or weakly attributed. For AI-driven search, this reduces selection chances. A strong Organization entity improves credibility, citation likelihood, and long-term AI recall.
How author and publisher entities support E-E-A-T
Author and publisher entities help AI evaluate Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. Author entities show who created the content and their qualifications. Publisher entities confirm who stands behind it.
When these entities are clearly defined and connected, AI can assess credibility faster. Missing or vague author signals weaken trust. Clear author and publisher schema strengthens AI confidence and improves answer eligibility.
Why AI relies on organization-level credibility signals
AI relies on organization-level signals because brands are more stable than individual pages. An established organization entity signals consistency and accountability.AI systems prefer citing sources with clear organizational backing. This reduces risk and improves answer reliability across queries.
How should Article schema be optimized for AI answers?
Article schema should be optimized to clearly define topic focus, entities, and relevance. Fields like headline, about, author, and publisher help AI understand what the article explains and why it matters.
For AI answers, clarity beats length. Article schema should align tightly with visible content. When stacked with Organization and FAQ schema, it becomes answer-ready. Poorly optimized Article schema often passes validation but fails to influence AI systems. Proper optimization improves extraction accuracy and citation frequency.
Using headline, about, mentions, and entity references
Headline should clearly reflect the main topic entity. The about property should reference the primary subject. Mentions can link supporting entities.These fields help AI map the article into its knowledge framework. Consistent entity references increase relevance and trust.
How to stack Article schema with FAQ schema correctly
Article schema should describe the main content, while FAQ schema highlights specific questions answered on the page. They should not duplicate information.When stacked correctly, Article provides context and FAQ provides extraction points. This combination improves AI answer generation and visibility.
Why FAQ schema is a high-impact AEO asset
FAQ schema is high-impact because it mirrors how users ask questions and how AI delivers answers. AI systems look for clear question-answer pairs.
When FAQ schema matches on-page headings and content, AI can extract answers confidently. Overuse or irrelevant FAQs reduce trust, but precise usage increases citation chances. FAQ schema is one of the fastest ways to improve AEO performance when used correctly.
How question-based H3/H4 align with FAQ schema
Question-based headings naturally map to FAQ schema. Each H3 or H4 question can become a structured FAQ item. This alignment reduces ambiguity and improves extraction accuracy. AI prefers clean question-answer structures.
How to avoid FAQ schema over-optimization
Avoid adding FAQs that are not visible or useful. Do not repeat the same question across pages.Over-optimization triggers trust issues. Focus on relevance and clarity instead of volume.
When should you use How To, Product, Review, and LocalBusiness schema?
These schemas should be used when content intent clearly matches user needs. How To fits instructional content. Product and Review fit transactional intent. Local Business fits location-based services.
AI engines classify intent before selecting schema signals. Matching schema to intent improves relevance and reduces confusion. Misaligned schema weakens understanding and harms visibility.
Mapping schema to informational vs transactional intent
Informational intent works best with Article, FAQ, and HowTo. Transactional intent fits Product and Review schema.Correct mapping helps AI deliver the right answer type. It also improves citation accuracy.
How AI engines detect and classify search intent
AI engines analyze queries, content structure, and schema signals together. Schema helps confirm intent quickly.Clear intent alignment increases chances of being selected for AI answers and summaries.
Schema Gap Analysis – The Strategy Competitors Rarely Use
Schema gap analysis is the process of finding missing or weak structured data that competitors use to win AI visibility. It matters because many sites add basic schema but never compare it against what actually appears in AI answers. In AI-driven search, gaps in schema often explain why similar content gets cited while yours does not.
In 2026, competitive advantage comes from precision, not volume. Schema gap analysis helps you see which schema types, entity links, and structures AI engines reward in your niche. The practical benefit is clear prioritization. Instead of guessing, you invest in schema that improves citations, trust, and answer inclusion. Most competitors skip this step, which makes it one of the fastest ways to gain AI and AEO visibility without creating new content.
What is schema gap analysis in competitive SEO?
Schema gap analysis is the comparison of your structured data against competitors that rank or appear in AI answers. It identifies missing schema types, weak entity signals, and poor stacking strategies.
This matters because AI engines often favor patterns. If top AI-cited pages consistently use certain schemas, those schemas are likely influencing visibility. Gap analysis shows what you lack and what to fix first. It turns schema optimization into a data-driven strategy instead of trial and error.
How to audit schema usage on top-ranking pages
Start by reviewing the structured data of top-ranking and AI-visible pages. Use schema inspection tools to identify schema types, entity references, and hierarchy.Look for repeated patterns across winners. Note what they use consistently and what you do not. This comparison reveals practical opportunities.
How to identify missing schema opportunities
Missing opportunities appear when competitors use schema types you do not. These may include FAQ, author entities, or stronger Organization references.Focus on gaps that align with your content. Do not add schema blindly. Relevance always comes first.
How do you analyze schema on AI-visible pages?
Analyzing AI-visible pages means studying content that appears in AI answers, not just SERPs. These pages often share strong entity signals and clean schema stacking.
AI-visible content usually has clear authorship, organization links, and answer-ready structures. Comparing these pages to yours highlights why AI selects them. This insight helps you optimize for answers, not just rankings.
Which pages appear in AI answers and why?
Pages in AI answers usually explain topics clearly, use structured headings, and include supportive schema. They also show strong entity consistency.AI selects them because they reduce ambiguity. Schema plays a major role in that clarity.
Common schema patterns across AI-cited content
Common patterns include Organization + Article + FAQ stacking, consistent @id usage, and clear author entities.These patterns repeat across industries, showing what AI systems prefer.
How do you build a schema prioritization roadmap?
A schema roadmap ranks schema tasks by impact and effort. Not all schema types deliver equal value.Start with high-impact schemas that influence trust and answers. Then expand into supporting types. This approach avoids wasted effort and accelerates results.
High-impact vs low-impact schema types
High-impact schemas include Organization, Article, FAQ, and entity references. Low-impact schemas are those unrelated to intent.Prioritize schemas that directly support AI understanding and answers.
How to prioritize schema based on SEO and AEO ROI
Evaluate schema based on visibility gains, not just validation. Focus on schemas linked to AI citations and zero-click answers.This ensures schema work delivers measurable SEO and AEO returns.
Advanced JSON-LD Best Practices for Schema Stacking
Advanced JSON-LD best practices focus on clarity, consistency, and safe layering of structured data for AI systems. JSON-LD is the preferred schema format because it separates structured data from visible content and is easier for AI to parse. In 2026, AI search engines rely heavily on clean JSON-LD to reduce errors and confirm entity relationships.
For Structured Data Stacking, best practices are not about adding more schema, but about adding smarter schema. Poorly written JSON-LD can confuse AI, even if it passes validation. Clean structure, shared entity IDs, and logical grouping improve AI trust and answer eligibility. The practical benefit is stronger AI visibility, fewer misinterpretations, and higher chances of citations across AI-driven search platforms.
Why is JSON-LD the preferred format for AI systems?
JSON-LD is preferred because it delivers explicit, machine-readable meaning without interfering with page layout. AI systems can process JSON-LD faster and more reliably than embedded formats. This matters because AI engines need clear signals at scale.
JSON-LD also supports complex relationships through @id and @graph. This makes it ideal for schema stacking. Unlike inline formats, JSON-LD reduces implementation errors and keeps content clean. For AI-driven search, this reliability improves trust and extraction accuracy.
Why Microdata and RDFa are declining in relevance
Microdata and RDFa are declining because they mix structured data with HTML. This increases implementation errors and maintenance risk. Small HTML changes can break schema unintentionally.
AI systems also struggle more with fragmented signals. JSON-LD keeps data centralized and consistent. As AI search evolves, clean separation of content and data becomes more important than ever.
How to write clean, AI-readable JSON-LD
Clean JSON-LD uses consistent entity IDs, accurate properties, and minimal redundancy. Each schema block should serve a clear purpose.
Avoid guessing values or copying templates blindly. Match schema exactly to visible content. This precision improves AI confidence and reduces trust loss.
How do you safely combine multiple schema blocks?
You can safely combine multiple schema blocks when they describe different layers of the same content. The key is consistency. Shared entities must use the same @id values across schemas.
Stacking works best when schemas support each other logically. Avoid duplicate entities with different IDs. When done correctly, AI merges signals instead of treating them as conflicts.
When and how to use @graph
@graph is useful when managing many related schemas. It allows multiple entities and schema types to exist in one structured block.Use @graph to define Organization, Website, WebPage, and Article together. This reduces duplication and keeps relationships clear. AI systems prefer this connected structure.
How to avoid duplicate or conflicting entities
Duplicates happen when the same entity is defined multiple times with different IDs. Conflicts happen when properties disagree.Prevent this by centralizing entity definitions. Reuse IDs consistently. Regular audits help catch errors early and protect AI trust.
Why schema validation goes beyond Rich Results testing
Passing Rich Results tests only confirms technical correctness. It does not confirm AI readiness. AI systems evaluate meaning, not just syntax.Schema must align with intent, content, and entities. Validation tools cannot judge that. Manual review is essential for advanced stacking strategies.
Search Console errors vs AI readiness
Search Console flags syntax and eligibility issues. It does not assess clarity or trust.A page can have zero errors and still fail in AI answers. AI readiness requires semantic alignment, not just clean reports.
A manual schema QA checklist for advanced SEO
Manual QA checks entity consistency, schema relevance, and stacking logic. It also compares schema against visible contentThis process ensures schema supports AI understanding, not just compliance.
Measuring Success – SEO & AI Visibility Metrics
Measuring success for Structured Data Stacking requires tracking both SEO performance and AI visibility signals. Traditional metrics alone no longer show the full impact. In AI-driven search, visibility often happens without clicks, so new measurement methods are essential. Structured data influences how content is interpreted, cited, and reused by AI systems.
In 2026, success means being present in AI answers, summaries, and citations, not just rankings. Schema improves eligibility for these placements, but only if results are tracked correctly. The practical benefit of proper measurement is clarity. You can see which schema improvements drive visibility and which do not. This allows smarter optimization decisions and better ROI from structured data investments.
How do you measure the SEO impact of structured data?
The SEO impact of structured data is measured through changes in impressions, CTR, and eligibility for enhanced results. Schema does not guarantee rankings, but it influences how results appear and how often they are clicked.
Track performance before and after schema changes. Look for improvements in impressions and rich result presence. Also monitor crawl behavior and indexing stability. Structured data often improves understanding, which can indirectly support rankings. Measuring these signals helps connect schema work to SEO outcomes instead of guessing its value.
Tracking CTR, impressions, and rich results
CTR and impressions show how schema affects visibility. Rich results often improve click behavior.Monitor Search Console enhancements and performance reports to see changes tied to schema updates.
Indexing and crawl signals influenced by schema
Clear schema helps crawlers understand content faster. This can improve crawl efficiency and indexing accuracy.Watch crawl stats and indexing reports for stability improvements after schema optimization.
How do you measure AI visibility with zero-click answers?
AI visibility is measured by tracking appearances in AI-generated answers, summaries, and citations. These do not always produce clicks, but they build brand authority and recall.
Manual monitoring of AI tools is often required. Look for consistent mentions, summaries, or sourced answers. Structured Data Stacking improves these signals by increasing trust and clarity. Measuring zero-click visibility helps align SEO with AEO goals.
Tracking AI citations and brand mentions
Track how often your brand or content is referenced in AI answers. This can be done through regular checks and monitoring tools.Increased citations signal stronger AI trust and relevance.
Why zero-click visibility is a core AEO KPI
Zero-click visibility reflects influence, not traffic. AI answers shape user decisions even without visits.For AEO, presence matters more than position. Schema-driven visibility supports long-term authority.
Common Structured Data Stacking Mistakes to Avoid
Common structured data stacking mistakes usually happen when schema is added without strategy or intent alignment. In AI-driven search, bad schema is worse than no schema because it creates confusion and trust issues. AI systems are strict about consistency, relevance, and accuracy. When schema sends mixed signals, AI engines reduce visibility or ignore the page completely.
In 2026, AI-first search rewards precision. Over-stacking, irrelevant schema, and entity conflicts are common reasons content fails to appear in AI answers. Avoiding these mistakes protects your authority and keeps your structured data trustworthy. The practical benefit is cleaner AI interpretation, stronger citation chances, and fewer long-term visibility losses caused by schema misuse.
Why over-stacking schema can hurt trust
Over-stacking schema hurts trust when too many schema types are added without clear relevance. AI systems expect schema to reflect real content, not inflated signals. Adding every possible schema type makes intent unclear.
When AI detects excessive or unnecessary schema, it reduces confidence in the page. Instead of improving visibility, over-stacking often causes schema to be ignored. The best practice is selective stacking. Each schema should have a clear purpose and support user intent. Quality and alignment matter more than quantity.
How spam signals are triggered
Spam signals are triggered when schema exaggerates content value or misrepresents page intent. Examples include adding FAQ schema without real questions or Product schema on non-product pages.
AI systems flag these patterns as manipulation. Once trust drops, recovery is slow. Accurate schema prevents spam classification.
How Google evaluates schema abuse
Google evaluates schema abuse by comparing structured data with visible content. Mismatches signal manipulation.Repeated abuse can lead to loss of rich results and reduced AI trust across the site.
Why irrelevant schema damages AI understanding
Irrelevant schema damages AI understanding because it introduces false context. AI relies on schema to reduce ambiguity. Incorrect schema does the opposite.
For example, using Review schema on informational content confuses intent. AI may misclassify the page or ignore it. Relevance ensures schema reinforces meaning instead of distorting it.
Content-schema mismatch examples
A common mismatch is adding LocalBusiness schema to a global informational page. Another is using HowTo schema on opinion content.These mismatches reduce clarity and weaken AI confidence.
How entity confusion reduces rankings and citations
Entity confusion happens when the same entity is defined differently across pages. AI struggles to reconcile conflicting signals.This confusion lowers authority and reduces citation frequency. Consistent entity definitions protect visibility.
The Future of Structured Data for AI Search (2026 & Beyond)
The future of structured data is tightly linked to how AI systems retrieve, verify, and reuse information in real time. In 2026 and beyond, structured data is no longer just a supporting SEO element. It becomes a core input for AI agents, answer engines, and autonomous search experiences. AI systems increasingly rely on clean entity graphs and structured context to reduce hallucinations and improve accuracy.
This shift matters because ranking alone will not guarantee visibility. AI-first search rewards brands that provide reliable, machine-readable truth. Structured Data Stacking enables this by feeding AI systems consistent entity relationships at scale. The practical benefit is long-term dominance in AI answers, summaries, and recommendations. Brands that invest early in strong schema foundations will be easier for AI to trust, remember, and cite repeatedly.
How Model Context Protocol (MCP) may change schema usage
Model Context Protocol may change schema usage by allowing AI models to consume structured data dynamically instead of statically. Instead of only reading schema at crawl time, AI agents could request structured context in real time. This makes accuracy and consistency even more important.
In this environment, sloppy or outdated schema becomes a liability. Clean structured data becomes an active data layer that feeds AI decisions. Schema will no longer be passive markup. It will function as live context for AI reasoning, retrieval, and summarization. Structured Data Stacking prepares sites for this shift by creating reliable, reusable entity structures that AI agents can safely consume.
How AI agents will consume structured data
AI agents will consume structured data as verified context when answering questions, completing tasks, or making recommendations. Schema will act as a trusted reference layer.
Agents will favor sources with consistent entities and clear relationships. This allows faster decisions with lower error risk.
Schema’s role in real-time AI retrieval
Schema will guide real-time retrieval by telling AI what content represents before reading full pages. This improves speed and accuracy.Well-stacked schema ensures content is selected early in AI response generation pipelines.
Will structured data become more important than rankings?
Structured data will become more important than rankings for visibility in AI answers. Rankings matter less when AI generates responses directly. What matters is whether your content is trusted enough to be used.
AI systems choose sources based on clarity, authority, and entity confidence. Structured data provides all three. This shift does not eliminate SEO, but it redefines success. Being referenced beats being ranked. Structured Data Stacking supports this new model.
The shift from SEO to AEO
SEO focused on clicks and positions. AEO focuses on answers and visibility. Structured data bridges this transition.Schema helps content move from search results into AI responses, summaries, and citations.
Why brands with strong entity graphs will dominate AI answers
Strong entity graphs help AI connect facts quickly and confidently. Brands with consistent entity signals become default references.Over time, AI systems reuse trusted entities more often. This compounds visibility and authority across AI platforms.
inal Takeaway – Structured Data Stacking as a Competitive Advantage
Structured Data Stacking is a competitive advantage because it aligns your content with how AI systems actually understand and select information. Basic schema is no longer enough in AI-first search. In 2026, visibility depends on clear entities, strong relationships, and trusted structured context. Stacked schema turns your site into a reliable data source, not just a collection of pages.
This approach matters because AI answers shape user decisions without clicks. When your content is consistently understood and trusted, it gets reused across answers, summaries, and citations. The practical benefit is durable visibility that competitors struggle to replicate. Structured Data Stacking is not a technical extra anymore. It is the backbone of modern AEO and AI-driven SEO strategies.
Why basic schema implementation is no longer enough
Basic schema implementation is no longer enough because it only describes isolated elements, not full context. AI systems do not rely on single signals. They look for confirmation across entities, pages, and relationships. A lone Article or FAQ schema rarely provides that depth.
As AI search matures, it favors sources that reduce uncertainty. Basic schema may validate, but it does not differentiate. Stacked schema builds clarity and authority at scale. This is why many sites with “valid” schema still fail to appear in AI answers. Without stacking, schema remains passive instead of influential.
Why structured data stacking is the backbone of AI-first SEO
Structured data stacking is the backbone of AI-first SEO because it feeds AI systems the structured truth they need. AI engines prioritize meaning, trust, and reuse. Stacked schema delivers all three through connected entities and consistent signals.
This approach supports zero-click visibility, AI citations, and long-term brand recall. Rankings may fluctuate, but trusted structured data compounds value. Sites with strong schema stacks become default references. This makes structured data stacking essential, not optional, for future-proof SEO.
What your next action steps should be
Your next steps should focus on clarity, consistency, and prioritization. Start by auditing existing schema and entity definitions. Fix inconsistencies before adding new layers. Then build a clear Organization, Website, and WebPage foundation.
Next, stack Article and FAQ schema where intent matches. Connect cluster pages through shared entities. Finally, measure AI visibility, not just traffic. If you want to speed this up, streamline your free site audit with using ClickRank’s Professional SEO Audit Tool. It helps uncover schema gaps and AI readiness issues fast. Try it now and turn structured data into a real competitive edge.
Structured data is standardized metadata added to a webpage that tells machines exactly what different pieces of content represent — such as an article, product, FAQ, or business. AI systems like Google SGE, ChatGPT, and Perplexity use structured data to interpret content more accurately, improving how they extract and cite answers.
FAQ schema is a type of structured data markup that labels question-and-answer pairs so search engines and AI systems can easily extract them. While Google has limited traditional FAQ rich results, FAQ markup still helps AI platforms identify and cite Q&A content in conversational answers, increasing your chances of appearing in AI-generated responses.
No. FAQ schema increases the probability that AI platforms will recognize and extract your Q&A content, but it does not guarantee citations. Content quality, topical relevance, and authority still play major roles alongside structured data.
JSON-LD is the recommended structured data format for both AI search and SEO because it is widely supported, easy to maintain, and preferred by major platforms like Google and other AI systems.
Yes. Structured data does not directly boost rankings by itself but makes it easier for AI systems to understand the context, entities, and relationships in your content — increasing the likelihood of being featured in AI answers and rich features.
Yes. Structured data guidelines require that any FAQ schema you add must reflect content that is visible to users on the page. Marking up questions that are not displayed can be ignored by search engines or even flagged as manipulative.What is structured data and why is it important for AI search?
What is FAQ schema and how does it help AI and SEO visibility?
Does adding FAQ schema guarantee that AI will use my content?
What structured data format should I use for the best AI compatibility?
Can structured data improve how AI interprets my content even if it does not change rankings?
Should FAQ content be visible to users when adding FAQ schema?