SEO Basics are the simple rules that help a website show up on search engines like Google. It teaches beginners how to use correct titles, descriptions, keywords, images, and links so search engines can easily understand the website.
Learning SEO basics helps students and new learners make websites more visible, get more visitors, and improve online results step by step.
Understanding Search & User Intent
Search and user intent explain why people use search engines and what outcome they expect. Every search reflects a goal finding information, reaching a brand, or completing an action. For SEO in 2026, search engines no longer reward pages just for matching keywords. They rank pages that solve the intent behind the search.
This matters because Google and AI search systems now evaluate meaning, context, and usefulness. If your content aligns with intent, it earns visibility. If it doesn’t, rankings drop even with perfect keywords.
Practically, understanding search intent helps you create the right page type, content depth, and structure. It reduces bounce rates, improves engagement, and increases trust signals that modern algorithms depend on.
What do people search for online?
People search online to solve problems, learn, compare options, or take action. Searches are driven by curiosity, urgency, or decision-making needs. In modern SEO, understanding what people search for is less important than why they search.
Search behavior has expanded beyond simple keywords. Users now search full questions, comparisons, and follow-up queries. AI-powered results reward pages that clearly match these needs.
From a practical SEO view, knowing what people search for helps you map content to real demand. It ensures your pages answer actual user questions instead of guessing topics based on volume alone. We’ll explore this deeper in our dedicated guide on What people search for.
Types of search queries (navigational, informational, transactional, commercial)
Search queries fall into four clear types based on intent. Navigational queries aim to reach a specific site or brand. Informational queries seek answers or explanations. Commercial queries compare options before buying. Transactional queries show readiness to act.
Search engines use these categories to decide which page format to rank. A blog post won’t rank for a transactional query, and a product page won’t rank for an informational one.
For SEO, matching query type prevents misalignment. It helps you choose the right page blog, landing page, or product and increases ranking stability and conversions.
Why understanding search intent is critical for SEO
Search intent is critical because Google ranks usefulness, not keywords. If your content doesn’t satisfy intent, rankings will decline even with strong backlinks or technical SEO.
Modern algorithms evaluate engagement, pogo-sticking, and satisfaction signals. Pages that solve intent keep users longer and send positive feedback to search systems.
Practically, intent-driven SEO improves content accuracy, reduces wasted traffic, and increases trust. It also supports future-proofing as AI search engines rely heavily on intent matching rather than keyword density alone.
How do people search today?
People now search in short bursts, conversations, and follow-up queries across devices. Search is no longer linear. Users start on mobile, continue on desktop, and ask AI tools for summaries.Search engines adapt results dynamically based on context, location, and past behavior. This makes static keyword targeting less effective.
For SEO, this means content must be flexible, conversational, and structured for multiple formats. We’ll explore this further in our guide on How people search and Search behaviour psychology.
Desktop vs mobile search behaviour
Mobile search dominates discovery, while desktop supports deeper research and conversions. Mobile users want fast answers and simple layouts. Desktop users expect depth and comparison.
Google indexes mobile-first, meaning your mobile experience defines rankings. Slow pages or cluttered layouts hurt visibility.From an SEO standpoint, optimizing for mobile improves crawlability, engagement, and conversion flow. It’s no longer a UX choice it’s a ranking requirement.
Voice search trends and impact on SEO
Voice search uses natural language and question-based queries. Users speak differently than they type, using longer phrases and conversational tone.Search engines return concise, direct answers for voice queries. This favors structured content, clear headings, and simple explanations.
For SEO, optimizing for voice improves featured snippet eligibility and AI answer visibility. It also aligns content with future conversational search growth.
Conversational queries & AI-powered search
AI-powered search understands context across multiple questions. Users ask follow-ups instead of repeating keywords.This shifts SEO from keyword pages to topic-based coverage. Content must answer related questions clearly and in sequence.
Practically, conversational optimization improves retrieval in AI systems and strengthens topical authority. You can get more detail in our Search intent models guide.
Why is search important for businesses?
Search is important because it connects businesses with high-intent users at the exact moment of need. Unlike ads, search traffic compounds over time.Organic visibility builds trust and brand recall. Paid traffic stops when budgets stop.
For businesses, SEO-driven search delivers sustainable growth, predictable leads, and long-term ROI. This is explored further in our guide on Why search is important and Why SEO matters for business.
Organic search vs paid search benefits
Organic search builds lasting visibility and credibility. Paid search offers speed and control but lacks permanence.Search engines favor organic results for trust. Users click them more often, especially for research and comparisons.
From a strategy view, organic search reduces acquisition costs and supports brand authority, while paid search supports short-term campaigns.
Impact on traffic, leads, and conversions
Search traffic is intent-driven, meaning users are already looking for solutions. This leads to higher-quality visits.When intent, content, and UX align, conversions increase naturally. SEO also supports every stage of the funnel.
Practically, strong search visibility improves lead quality, lowers bounce rates, and increases lifetime customer value.
Why do people visit websites today?
People visit websites to get answers, evaluate trust, and complete tasks quickly. Patience is low, and expectations are high.Users judge credibility in seconds based on design, speed, and clarity. Content must prove value immediately.
For SEO, meeting these expectations improves engagement metrics that directly influence rankings. We explore this more in Why people visit websites and Digital information retrieval systems.
Content expectations (quality, relevance, speed)
Users expect accurate, relevant, and fast-loading content. Thin or outdated pages lose trust instantly.Search engines measure satisfaction through engagement and return behavior.Practically, high-quality content improves dwell time, repeat visits, and algorithmic trust signals.
User experience signals for ranking
UX signals include page speed, readability, navigation, and interaction clarity. These signals influence rankings directly and indirectly.Google rewards pages that feel effortless to use.
For SEO, improving UX increases retention, supports mobile-first indexing, and strengthens long-term visibility.
Core SEO Concepts
SEO is the system that helps search engines discover, understand, and rank your content so it reaches the right users at the right time. At its core, SEO connects user intent with relevant webpages through technical signals, content clarity, and authority signals.
In modern search, SEO is no longer about tricks or shortcuts. It’s about building pages that search engines can confidently recommend. Algorithms now evaluate structure, meaning, usefulness, and trust especially for long-term visibility in AI-driven results.
Practically, understanding core SEO concepts helps you make better decisions. You stop guessing and start building pages that are crawlable, indexable, and aligned with how search engines actually work today.
What is SEO and how does it work?
SEO works by optimizing content and websites so search engines can process and rank them accurately. When a user searches, search engines scan their index to find the most relevant and trustworthy results.
SEO connects three systems: search engines, content, and users. If one fails, rankings suffer. Keywords alone no longer work without structure, context, and authority.
For practical SEO, knowing how SEO works helps you avoid wasted effort. You focus on signals that matter crawl access, clarity, intent match, and trust rather than outdated tactics. We explore this further in our guide on How SEO works.
Crawling, indexing, ranking explained
Crawling is how search engines discover pages. Indexing is how they store and understand content. Ranking is how they decide which page appears first.If a page can’t be crawled, it won’t rank. If it’s crawled but poorly indexed, it won’t perform. Ranking only happens after the first two steps succeed.
From an SEO standpoint, this means technical setup matters before content promotion. Fixing crawl and index issues often delivers faster SEO gains than chasing new keywords.
Overview of search engine algorithms
Search engine algorithms are rule-based systems that evaluate relevance, quality, and trust. They analyze content meaning, links, engagement, and technical health.
Modern algorithms use machine learning to interpret intent, not just words. They reward pages that satisfy users completely.Practically, algorithm awareness helps you align content with long-term ranking signals. It also reduces panic during updates because strong fundamentals remain stable.
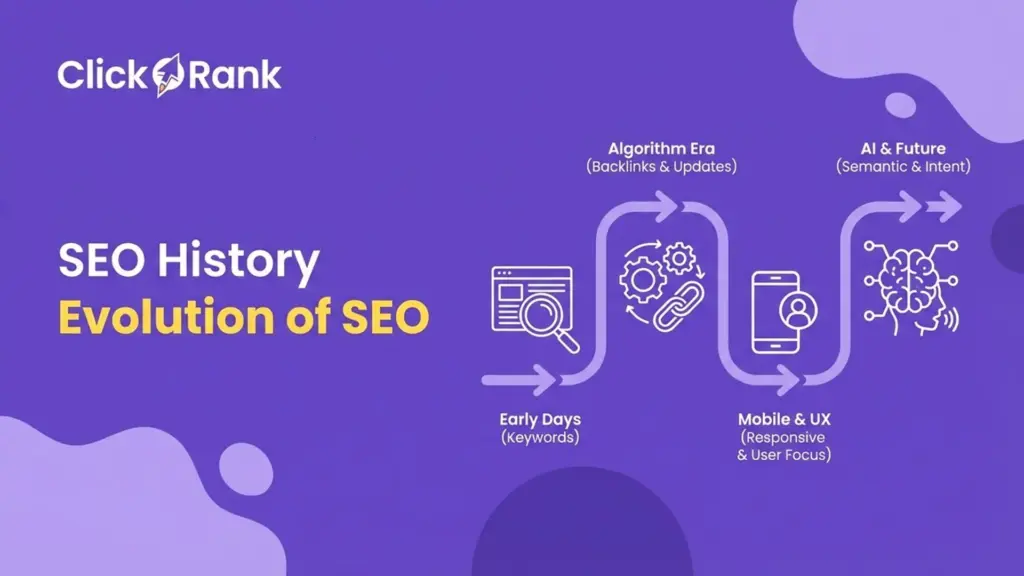
How has SEO evolved over time?
SEO has evolved from keyword matching to intent and trust evaluation. Early SEO rewarded keyword repetition. Modern SEO rewards clarity, authority, and experience.
Search engines now understand topics, entities, and relationships. This shift makes SEO more stable but also more demanding.Understanding SEO evolution helps future-proof strategies. We’ll explore this deeper in our SEO history and Search engine fundamentals guides.
History of SEO (1990s → today)
In the 1990s, SEO focused on meta tags and keyword density. The 2000s introduced link-based ranking.
From 2010 onward, Google emphasized quality, intent, and user experience. AI-driven systems now interpret meaning at scale.Practically, this history explains why shortcuts fail. Sustainable SEO aligns with how search engines mature over time.
Major Google updates and their impact
Major updates like Panda, Penguin, Hummingbird, Pigeon, and recent Helpful Content Update reshaped SEO.
These updates penalized low-quality content, spam links, and poor intent matching. They rewarded expertise and usefulness.Understanding updates helps with SEO recovery guides, algorithm rollback analysis, and long-term resilience against volatility.
Types of webpages for SEO
Different webpage types serve different intents. SEO success depends on matching page type to search intent.
Blogs educate, landing pages convert, product pages sell, and category pages organize. Mixing roles confuses users and algorithms.From a strategy view, correct page types improve rankings and conversions. Explore this further in our Types of webpages guide.
Landing pages, blog posts, product pages, category pages
Landing pages target conversions. Blog posts target information. Product pages target transactions. Category pages support discovery.Search engines expect specific structures for each. Misalignment reduces performance.Practically, choosing the right page type simplifies SEO and improves user satisfaction signals.
Evergreen content vs timely content
Evergreen content stays relevant long-term. Timely content captures short-term demand.Both matter for SEO. Evergreen builds authority. Timely content captures trends.Balancing both supports consistent traffic and topical relevance over time.
Meet search engines – How they operate
Search engines are digital information retrieval systems that organize the web. Each engine prioritizes signals differently.Google dominates, but Bing, DuckDuckGo, and AI-powered engines matter for visibility diversification.
Understanding how engines operate helps expand reach beyond one platform.
Google, Bing, DuckDuckGo, AI-powered search engines
Google focuses on relevance and authority. Bing emphasizes structure and clarity. DuckDuckGo values privacy.AI-powered engines prioritize answer accuracy and context.For SEO, multi-engine optimization improves resilience and future readiness.
How ranking differs across engines
Ranking factors vary slightly across engines. Google favors engagement signals. Bing favors metadata and links.AI engines favor clarity, structure, and trust.Practically, writing clear, structured content performs well everywhere.
Learning SEO: Where to start
Learning SEO starts with foundations, not tactics. Beginners should understand search behavior, intent, and structure first.Tools and techniques come later. Strategy always comes first.This approach prevents overwhelm and builds durable skills. We explore this in Search behaviour psychology and SEO learning paths.
Step-by-step roadmap for beginners
Start with search intent. Learn page structure. Understand crawling basics. Then move to content and links.Avoid advanced tactics early. Master fundamentals first.This roadmap builds confidence and avoids common mistakes.
Recommended tools and resources
Beginners should start with Search Console, basic analytics, and content tools.Avoid tool overload. Focus on understanding data, not chasing metrics.Tools support SEO but strategy drives results.
SEO myths & misconceptions
SEO myths persist because shortcuts are tempting. SEO is not dead, instant, or automatic.Search engines reward effort, clarity, and trust not hacks.Debunking myths helps focus on what actually works. Explore more from our SEO myths.
Common myths debunked (e.g., “SEO is dead”)
SEO isn’t dead it’s evolved. Rankings don’t disappear overnight without reason.More content doesn’t guarantee traffic. Links alone don’t fix poor pages.Understanding myths prevents wasted effort and sets realistic expectations.
Keyword & Content Strategy
Keyword and content strategy define how your pages connect user intent with search engine understanding. Keywords tell search engines what a page is about, while content proves whether it deserves to rank. In 2026, SEO basics are no longer about stuffing phrases they’re about aligning meaning, structure, and usefulness.
Search engines now evaluate topics, entities, and satisfaction signals together. A strong strategy ensures your content is discoverable, understandable, and competitive across classic search and AI-powered results.
Practically, mastering keyword and content strategy prevents wasted effort. It helps you create pages that rank faster, last longer, and support internal linking, topical authority, and long-term SEO growth.
Why keywords matter in SEO
Keywords matter because they bridge user searches and your content. They help search engines match pages to queries and help users recognize relevance instantly. Even with AI-driven search, keywords remain the entry point for discovery.
Modern SEO basics treat keywords as signals, not targets. Search engines look at how naturally keywords fit into a topic, not how often they appear. Misusing keywords now hurts rankings.
From a practical angle, correct keyword usage improves visibility, click-through rates, and content alignment. We explore this deeper in our dedicated guide on What people search for.
Role of keywords in search visibility
Keywords signal relevance. They appear in titles, headings, URLs, and content to clarify meaning for crawlers.Search engines cross-check keyword usage with context and engagement. If users respond well, visibility improves.Practically, well-placed keywords help pages enter the right ranking pool without forcing unnatural phrasing.
Keyword types: short-tail, long-tail, LSI keywords
Short-tail keywords bring volume but high competition. Long-tail keywords capture intent and convert better. LSI keywords support topic understanding.Search engines use these variations to confirm topical depth.
For SEO basics, combining all three creates balanced traffic, stronger relevance, and better long-term rankings.
How to do keyword research effectively
Effective keyword research means finding intent, not just volume. It starts with understanding user problems and mapping them to queries.
Modern workflows prioritize relevance, competition, and intent alignment. Volume alone no longer predicts success.Practically, good keyword research reduces content rewrites and improves ROI. We’ll explore this fully in our How people search and Search intent models guides.
Tools & workflow (Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, SEMrush)
Keyword tools help surface demand and competition. Popular options include Google Keyword Planner, ClickRank, Ahrefs, and SEMrush.The workflow is simple: start broad, filter by intent, analyze competitors, then validate relevance.Tools support decisions but strategy determines outcomes.
Search intent mapping
Search intent mapping aligns keywords to page types and user goals. Informational queries map to guides. Transactional queries map to product pages.
Search engines expect this alignment. Mismatch causes ranking failure.Practically, intent mapping improves engagement, conversions, and ranking stability.
Why content quality is critical for SEO
Content quality is critical because search engines reward usefulness, not length. High-quality content satisfies intent fully and keeps users engaged.
Algorithms now evaluate depth, clarity, and accuracy. Thin or repetitive content loses trust quickly.From an SEO basics perspective, quality content compounds results. It earns links, rankings, and AI citations over time.
Content relevance, depth, and user engagement
Relevance answers the question. Depth solves the problem. Engagement proves satisfaction.Search engines track dwell time, scrolling, and return visits.Practically, focusing on engagement improves both rankings and conversions naturally.
Semantic content and entity-based targeting
Semantic content covers topics, not just keywords. Entity-based targeting helps search engines understand relationships.This approach aligns with AI-powered search and knowledge systems.
For SEO, semantic coverage builds topical authority and future-proofs rankings. Further knowledge tak from our Digital information retrieval systems guide.
How to structure content for search engines
Content structure helps search engines parse and prioritize information. Clear hierarchy improves crawlability and user comprehension.Search engines prefer predictable, logical layouts.Practically, structured content ranks faster and performs better across devices and formats.
Headers, subheaders, meta descriptions
Headers define hierarchy. Subheaders improve scannability. Meta descriptions improve clicks.Search engines use these elements to understand page focus.Correct structure boosts visibility without adding extra content.
Internal linking & topic clusters
Internal linking connects related content into topic clusters. This strengthens authority and crawl efficiency.Clusters signal expertise and improve page discovery.
Practically, internal links increase rankings site-wide. Take information from our Topic cluster strategy guide.
Links & Authority Building
Links and authority building explain why some pages rank consistently while others never break through. Search engines use links as trust signals to judge credibility, relevance, and importance. In modern SEO basics, authority is no longer about link quantity it’s about link quality, context, and consistency.
Today’s algorithms evaluate how pages are referenced across the web and within your own site. Links act like votes, but not all votes carry the same weight. A few relevant, trusted links outperform hundreds of weak ones.
Practically, strong authority building improves ranking stability, speeds up indexing, and protects sites during algorithm updates. It also supports long-term growth by compounding trust over time instead of relying on short-term tactics.
Why links are important for SEO
Links are important because they help search engines measure trust and discover content. External links show credibility. Internal links show structure and importance.
Search engines use links to understand how pages relate to each other. Without links, even great content can remain invisible.
From an SEO basics perspective, links turn content into a connected system. They help pages rank faster, spread authority, and improve crawl efficiency across the site.
Backlinks and their role in authority
Backlinks are links from other websites pointing to your page. They act as endorsements.Search engines evaluate backlink quality based on relevance, trust, and context. One strong backlink can outweigh dozens of weak ones.
Practically, earning backlinks through useful content builds sustainable authority and improves rankings across related pages.
Internal linking strategies
Internal links connect pages within your website. They guide crawlers and users.Strategic internal linking distributes authority, clarifies topic relationships, and improves user navigation.For SEO, internal links are fully controllable and often the fastest way to improve rankings site-wide.
Understanding search authority
Search authority is the level of trust a search engine assigns to a page or website. It’s built over time through consistent quality signals.Authority affects how easily new pages rank and how resilient a site is during updates.
Understanding authority helps prioritize efforts. You stop chasing quick wins and start building long-term credibility. Take more information from Search engine fundamentals.
Page authority vs domain authority
Page authority reflects the strength of a single page. Domain authority reflects the overall site.Strong domains help new pages rank faster, but weak pages can still fail.Practically, SEO success comes from building both page-level relevance and site-wide trust.
How trust and credibility impact rankings
Trust signals include content accuracy, links, engagement, and brand consistency.Search engines reduce visibility for sites with misleading or low-quality signals.For SEO, trust is cumulative. Every good page strengthens the whole site.
SEO success factors
SEO success depends on multiple systems working together, not one isolated tactic. Links alone won’t fix weak content. Content alone won’t rank without authority.
Modern SEO basics require balance across content, links, UX, and technical health.Understanding these factors helps avoid over-optimization and wasted effort.
Content, links, UX, technical performance
Content solves intent. Links prove credibility. UX keeps users engaged. Technical performance enables access.If one fails, rankings suffer.Practically, auditing all four areas delivers the most reliable SEO improvements.
Metrics to track success
SEO success is measured through visibility, engagement, and conversions not rankings alone.Key metrics include organic traffic quality, crawl health, indexed pages, and user behavior.Tracking the right metrics helps guide strategy and supports recovery after updates or ranking drops.
SEO Strategy & Frameworks
SEO strategy defines how all SEO efforts connect to business outcomes, not just rankings. While tactics change frequently, strategy provides direction and consistency. In modern SEO basics, success comes from systems, not isolated actions.
Search engines reward sites that show long-term intent, consistent improvement, and user-focused growth. A strong framework helps teams adapt to algorithm updates without losing momentum.
Practically, strategy prevents random execution. It helps you prioritize what to optimize, when to optimize it, and how to measure progress across content, authority, and experience.
Strategy vs tactics – What’s the difference?
Strategy answers why and what. Tactics answer how. Strategy sets direction. Tactics execute steps.Without strategy, tactics become reactive. Without tactics, strategy never materializes.
For SEO basics, understanding this difference avoids burnout and wasted effort. It ensures every action supports a larger goal. You can explore this deeper in our Why SEO matters for business guide.
Long-term planning vs short-term action
Long-term planning focuses on authority, content depth, and trust. Short-term actions focus on quick fixes and optimizations.Both matter. Planning builds resilience. Actions create momentum.Practically, combining both ensures steady growth without sacrificing future stability.
Integrating SEO with marketing strategy
SEO should align with branding, content, and conversion goals. Disconnected SEO creates traffic without impact.Search visibility supports every marketing channel.Integrating SEO ensures consistency, higher ROI, and clearer measurement across teams.
Agile SEO – From planning to action
Agile SEO focuses on continuous improvement instead of rigid plans. It adapts quickly to performance data and algorithm changes.Search environments change constantly. Agile systems respond without panic.
Practically, agile SEO improves speed, reduces risk, and encourages experimentation. We explore this further in our SEO recovery guide and Algorithm rollback analysis.
Iterative optimization and testing
Iterative optimization means testing small changes, measuring results, and refining continuously.This reduces risk and improves learning.For SEO basics, iteration beats one-time optimization every time.
Team workflows for SEO execution
SEO execution requires clear workflows. Content, technical, and analytics teams must align.Clear roles prevent delays and duplication.Practically, good workflows turn strategy into consistent results.
See-Think-Do-Care SEO framework
The See-Think-Do-Care framework maps content to user awareness and intent stages. It aligns SEO with real buyer journeys.Search engines reward this alignment because it improves satisfaction.
Using this framework ensures coverage across the funnel. You can explore this more in our Search intent models guide.
Mapping content to buyer journey
See content builds awareness. Think content educates. Do content converts. Care content retains.Each stage requires different formats and intent focus.Practically, this mapping improves engagement and lifetime value.
Measuring success at each stage
Success metrics differ by stage. Visibility matters early. Conversions matter later.Search engines track these behaviors.Measuring correctly prevents misjudging SEO performance.
SEO strategy trade-offs
Every SEO decision involves trade-offs. Resources are limited. Priorities matter.Choosing depth over breadth, quality over quantity, or speed over scale affects outcomes.Understanding trade-offs helps maximize ROI. You can explore further in our Search engine fundamentals guide.
Prioritizing resources & effort for maximum ROI
High-impact pages deserve priority. Low-impact tasks get deprioritized.This focus improves efficiency.Practically, prioritization turns SEO from busywork into growth engine.
User Experience & Best Practices
User experience (UX) and SEO now work as one system, not two separate disciplines. Search engines rank pages that are easy to use, fast to load, and clear to understand. In modern SEO basics, UX is no longer optional it directly influences visibility, engagement, and trust.
Google and AI-driven search systems analyze how users interact with pages. If users struggle, leave quickly, or feel confused, rankings drop even if content is relevant. UX signals act as quality validators.
Practically, strong UX improves rankings, conversions, and retention at the same time. It also protects sites during updates like the Helpful Content Update, where satisfaction matters more than tactics.
How SEO and UX collide
SEO and UX collide because both aim to satisfy users. SEO brings users to a page. UX determines whether they stay, engage, or convert. If UX fails, SEO performance collapses.
Search engines now measure usability signals such as speed, layout stability, and readability. These signals influence rankings indirectly and directly.
For SEO basics, aligning UX with SEO ensures traffic turns into value. We explore this further in our Why people visit websites and Search behaviour psychology guides.
Page speed & mobile-friendliness
Page speed affects rankings, engagement, and conversions. Slow pages lose users before content loads.Mobile-friendliness is critical because Google uses mobile-first indexing. If mobile UX fails, rankings suffer everywhere.Practically, fast and mobile-optimized pages improve crawl efficiency, reduce bounce rates, and increase trust signals.
Navigation, layout, and readability
Clear navigation helps users and crawlers understand structure. Clean layouts reduce friction. Readability keeps users engaged.Search engines evaluate interaction patterns to infer satisfaction.
For SEO, improving layout and clarity increases dwell time and page depth both strong performance indicators.
Common SEO mistakes and how to fix them
Most SEO failures come from basic mistakes, not advanced problems. These issues block crawlers, confuse users, or dilute relevance.Fixing fundamentals often produces the fastest SEO gains.
Understanding common mistakes helps prevent ranking loss and supports recovery after updates. We explore this further in our SEO recovery guide help.
Duplicate content, broken links, missing meta tags
Duplicate content confuses search engines. Broken links damage trust. Missing meta tags reduce click-through rates.Search engines may index the wrong version or ignore pages entirely.Practically, regular audits and cleanup improve crawl health and ranking consistency.
Poor keyword targeting & over-optimization
Targeting the wrong keywords brings the wrong users. Over-optimization triggers quality filters.Search engines now detect unnatural patterns easily.For SEO basics, focusing on intent and natural language prevents penalties and improves long-term stability.
Webmaster guidelines every site should follow
Webmaster guidelines define what search engines expect from quality websites. Ignoring them increases risk of penalties or suppression.These guidelines cover indexing rules, content quality, link practices, and technical standards.
Following them aligns sites with long-term ranking systems rather than short-term exploits. We explore this deeper in our Webmaster guidelines.
Google guidelines, indexing rules, penalties
Google outlines clear rules on crawl access, quality standards, and spam practices.Violations can lead to manual actions or algorithmic demotion.Practically, compliance reduces volatility and improves trust across updates.
Tools to monitor compliance (Search Console, Bing Webmaster)
Monitoring tools reveal crawl issues, indexing errors, and policy warnings. Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools provide visibility into search health.These tools help diagnose problems early.For SEO, regular monitoring prevents silent failures and supports proactive optimization.
Learning SEO & Career Path
Learning SEO is about building durable skills, not memorizing tactics. Search engines change, but the fundamentals intent, relevance, trust, and experience remain stable. In modern SEO basics, strong professionals understand systems, not shortcuts.
SEO careers now span content, technical optimization, analytics, strategy, and AI search. This makes SEO a long-term, flexible career path with growing demand across industries.
Practically, learning SEO the right way helps you avoid burnout, stay employable, and adapt as algorithms evolve. It also positions you to work on higher-impact strategy instead of routine execution.
How to become an SEO expert
Becoming an SEO expert requires progressive learning and real-world practice. Mastery comes from understanding why things work, not just how to do them.Experts think in systems search behavior, intent models, content architecture, and authority signals.
For SEO basics, following a clear learning path prevents overwhelm and accelerates growth. We explore this deeper in our Learning SEO and Search engine fundamentals guides.
Learning roadmap (beginner → intermediate → advanced)
Beginners learn intent, keywords, and page structure. Intermediate learners master technical SEO, content strategy, and links. Advanced SEOs focus on systems, scaling, and AI-driven search.
Each stage builds on the last.Practically, this roadmap ensures skills compound instead of resetting with every update.
Certifications and courses
Certifications help structure learning but don’t replace experience. Courses provide frameworks, not rankings.Search engines don’t reward certificates they reward outcomes.For SEO, choose education that teaches thinking, testing, and analysis rather than hacks.
SEO conferences and events worth attending
SEO events matter because search evolves in public before it’s documented. Conferences reveal trends, case studies, and failures early.They also connect you with practitioners solving real problems.
For career growth, events provide insight beyond blogs and tutorials. You can learn further in our SEO community and learning.
Networking, latest trends, workshops
Networking accelerates learning. Workshops provide hands-on experience.Trends discussed at events often shape future updates.Practically, connections and shared knowledge often outperform solo learning.
Continuous learning in SEO
SEO requires continuous learning because algorithms, platforms, and user behavior change constantly. Static knowledge becomes outdated quickly.
Successful SEOs test, measure, and adapt.This mindset keeps skills relevant and resilient. We explore this further in our Continuous SEO learning guide.
Keeping up with algorithm updates
Google releases frequent updates, including core updates and spam changes.Tracking patterns matters more than reacting emotionally.For SEO basics, understanding update intent helps guide calm, effective responses.
Experimenting with new tools & strategies
Experimentation builds intuition. Tools evolve, but testing reveals what actually works.Controlled experiments reduce risk and improve learning speed.Practically, experimentation turns theory into expertise.
Future of SEO
The future of SEO is driven by AI understanding, intent accuracy, and experience quality, not mechanical optimisation. Search engines are shifting from ranking pages to delivering answers, summaries, and recommendations across multiple formats. In modern SEO basics, visibility matters more than position.
Machine learning now evaluates meaning, trust, and usefulness at scale. This reduces the impact of shortcuts and increases the value of clear, authoritative content. SEO is becoming more predictive and less reactive.
Practically, understanding where SEO is heading helps you prepare content, structure, and strategy for long-term relevance especially as AI-powered search becomes the default discovery layer.
AI, ML, and modern search engines
AI and machine learning power how modern search engines interpret intent, context, and quality. They no longer rely only on static ranking factors.Search engines learn from user behavior, patterns, and outcomes. This makes SEO more holistic and less formulaic.
For SEO basics, this means focusing on clarity, trust, and completeness rather than manipulation. We explore this deeper in our Digital information retrieval systems and Search engine fundamentals page learn more.
AI-driven SEO strategies
AI-driven SEO strategies focus on topic coverage, intent satisfaction, and content clarity. They prioritize answering questions fully and accurately.Search engines reward pages that reduce follow-up searches.Practically, AI-aligned SEO improves stability, visibility in answer engines, and future-proof rankings.
AI content optimisation and retrieval SEO
Retrieval SEO optimizes content so AI systems can easily extract and reuse it. This includes clear structure, concise answers, and semantic consistency.AI engines favor content they can trust and cite.
For SEO, retrieval optimization increases presence in AI summaries, snippets, and conversational search results.
Mobile, voice, and visual search
Search is no longer text-only. Users search through voice, images, and mobile-first experiences. Each format changes how content is discovered and displayed.Search engines adapt results based on device and context.
For SEO basics, preparing for these formats ensures visibility beyond traditional SERPs. We explore this further in our How people search guide.
Preparing content for new search formats
New formats require concise answers, structured sections, and fast-loading pages. Voice and AI search favor direct responses.Mobile-first layouts remain critical.Practically, optimizing for formats improves reach and engagement across devices.
Multimodal search optimisation
Multimodal search combines text, images, and context. Users can search with photos, voice, and follow-up questions.Search engines connect these signals into one experience.For SEO, multimodal optimisation increases discoverability and aligns content with how users naturally search today.
What is SEO and why is it important?
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is the process of improving a website so it ranks higher in search engine results pages (SERPs), driving more organic (unpaid) traffic and visibility. It matters because higher rankings lead to more clicks, brand exposure, and potential customers without paying for ads.
How do search engines like Google work?
Search engines use bots (crawlers) to discover and index pages across the web. They evaluate relevance and authority using algorithms to decide what content to show for each query. The result is a ranked list of pages based on hundreds of ranking signals.
What are keywords and how do they influence SEO?
Keywords are the terms users type into search engines. They guide SEO by helping you understand search intent and match your content to user needs. Effective keyword research ensures your pages show up for relevant search queries.
What is the difference between on-page SEO and off-page SEO?
On-page SEO refers to optimizations you make on your website (content, meta tags, headings, images). Off-page SEO includes external signals like backlinks from other websites that increase your authority and trust.
What is technical SEO and why does it matter?
Technical SEO refers to backend website optimizations such as improving site speed, ensuring mobile-friendliness, fixing crawl errors, and structured data markup. It helps search engines crawl and index your pages efficiently.
How long does it take for SEO to show results?
SEO typically takes time because search engines need to crawl, index, and evaluate changes. Most beginners start seeing measurable improvements within 3–6 months, but competitive niches may take longer.
Why do some websites rank higher than others?
Ranking depends on relevance, authority, user experience, backlinks, content quality, and technical strength. Search engines prioritize pages that best satisfy intent, are trusted by users, and have strong supporting signals.
What are common SEO mistakes to avoid?
Some frequent pitfalls include keyword stuffing, duplicate content, broken links, poor mobile experience, ignoring metadata, and neglecting page speed all of which can hurt visibility and performance.
What tools can beginners use to learn and track SEO?
Popular tools for beginners include Google Search Console, Google Analytics, Ahrefs, SEMrush, Moz, and keyword research tools that help analyze performance, track rankings, and find keyword opportunities.
How do search intent and content relevance affect SEO?
Content that aligns with user intent (informational, transactional, navigational) performs better because search engines aim to match the best answer to what users are actually seeking. Understanding intent allows you to tailor content that both users and algorithms value.